Legend:
 Definition Definition
 Field Listing Field Listing
 Rank Order Rank Order
|
Background:
|


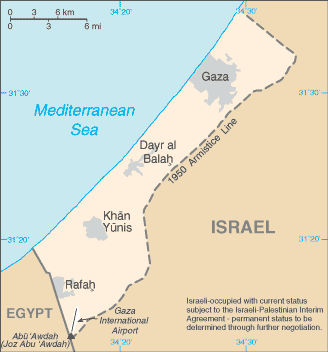
The Israel-PLO Declaration of Principles on Interim Self-Government Arrangements (the DOP), signed in Washington on 13 September 1993, provided for a transitional period not exceeding five years of Palestinian interim self-government in the Gaza Strip and the West Bank. Under the DOP, Israel agreed to transfer certain powers and responsibilities to the Palestinian Authority, which includes the Palestinian Legislative Council elected in January 1996, as part of the interim self-governing arrangements in the West Bank and Gaza Strip. A transfer of powers and responsibilities for the Gaza Strip and Jericho took place pursuant to the Israel-PLO 4 May 1994 Cairo Agreement on the Gaza Strip and the Jericho Area and in additional areas of the West Bank pursuant to the Israel-PLO 28 September 1995 Interim Agreement, the Israel-PLO 15 January 1997 Protocol Concerning Redeployment in Hebron, the Israel-PLO 23 October 1998 Wye River Memorandum, and the 4 September 1999 Sharm el-Sheikh Agreement. The DOP provides that Israel will retain responsibility during the transitional period for external and internal security and for public order of settlements and Israeli citizens. Direct negotiations to determine the permanent status of Gaza and West Bank that began in September 1999 after a three-year hiatus, were derailed by a second intifadah that broke out in September 2000. The resulting widespread violence in the West Bank and Gaza Strip, Israel's military response, and instability within the Palestinian Authority continue to undermine progress toward a permanent agreement. Following the death of longtime Palestinian leader Yasir ARAFAT in November 2004, the election of his successor Mahmud ABBAS in January 2005 could bring a turning point in the conflict.
|
|
Population:
|



1,324,991
note: in addition, there are more than 5,000 Israeli settlers in the Gaza Strip (July 2004 est.)
|
|
Age structure:
|


0-14 years: 49% (male 332,582; female 316,606)
15-64 years: 48.3% (male 326,450; female 314,098)
65 years and over: 2.7% (male 14,847; female 20,408) (2004 est.)
|
|
Median age:
|


total: 15.5 years
male: 15.3 years
female: 15.6 years (2004 est.)
|
|
Population growth rate:
|


3.83% (2004 est.)
|
|
Birth rate:
|



40.62 births/1,000 population (2004 est.)
|
|
Death rate:
|



3.95 deaths/1,000 population (2004 est.)
|
|
Net migration rate:
|


1.6 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2004 est.)
|
|
Sex ratio:
|


at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.73 male(s)/female
total population: 1.04 male(s)/female (2004 est.)
|
|
Infant mortality rate:
|



total: 23.54 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 24.71 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 22.31 deaths/1,000 live births (2004 est.)
|
|
Life expectancy at birth:
|



total population: 71.59 years
male: 70.31 years
female: 72.94 years (2004 est.)
|
|
Total fertility rate:
|



6.04 children born/woman (2004 est.)
|
|
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:
|



NA
|
|
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:
|



NA
|
|
HIV/AIDS - deaths:
|



NA
|
|
Nationality:
|


noun: NA
adjective: NA
|
|
Ethnic groups:
|


Palestinian Arab and other 99.4%, Jewish 0.6%
|
|
Religions:
|


Muslim (predominantly Sunni) 98.7%, Christian 0.7%, Jewish 0.6%
|
|
Languages:
|


Arabic, Hebrew (spoken by Israeli settlers and many Palestinians), English (widely understood)
|
|
Literacy:
|


definition: NA
total population: NA
male: NA
female: NA
|
|
Country name:
|


conventional long form: none
conventional short form: Gaza Strip
local long form: none
local short form: Qita Ghazzah
|
|
Economy - overview:
|


Economic output in the Gaza Strip - under the responsibility of the Palestinian Authority since the Cairo Agreement of May 1994 - declined by about one-third between 1992 and 1996. The downturn was largely the result of Israeli closure policies - the imposition of generalized border closures in response to security incidents in Israel - which disrupted previously established labor and commodity market relationships between Israel and the WBGS (West Bank and Gaza Strip). The most serious negative social effect of this downturn was the emergence of high unemployment; unemployment in the WBGS during the 1980s was generally under 5%; by 1995 it had risen to over 20%. Israel's use of comprehensive closures decreased during the next few years and, in 1998, Israel implemented new policies to reduce the impact of closures and other security procedures on the movement of Palestinian goods and labor. These changes fueled an almost three-year-long economic recovery in the West Bank and Gaza Strip; real GDP grew by 5% in 1998 and 6% in 1999. Recovery was upended in the last quarter of 2000 with the outbreak of violence, triggering tight Israeli closures of Palestinian self-rule areas and a severe disruption of trade and labor movements. In 2001, and even more severely in 2002, Israeli military measures in Palestinian Authority areas resulted in the destruction of capital plant and administrative structure, widespread business closures, and a sharp drop in GDP. Including West Bank, the UN estimates that more than 100,000 Palestinians out of the 125,000 who used to work in Israel, in Israeli settlements, or in joint industrial zones have lost their jobs. In addition, about 80,000 Palestinian workers inside the Territories are losing their jobs. International aid of $2 billion in 2001-02 to the West Bank and Gaza Strip prevented the complete collapse of the economy and allowed Finance Minister Salam FAYYAD to implement several financial and economic reforms. Budgetary support, however, was not as forthcoming in 2003.
|
|
GDP:
|



purchasing power parity - $768 million (2003 est.)
|
|
GDP - real growth rate:
|



4.5% (2003 est.)
|
|
GDP - per capita:
|



purchasing power parity - $600 (2003 est.)
|
|
GDP - composition by sector:
|


agriculture: 9%
industry: 28%
services: 63% (includes West Bank) (2002 est.)
|
|
Population below poverty line:
|


60% (2003 est.)
|
|
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
|


lowest 10%: NA
highest 10%: NA
|
|
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
|



2.2% (includes West Bank) (2001 est.)
|
|
Labor force:
|



NA (1997)
|
|
Labor force - by occupation:
|


agriculture 13%, industry 21%, services 66% (1996)
|
|
Unemployment rate:
|



50% (includes West Bank) (2003 est.)
|
|
Budget:
|


revenues: $676.6 million
expenditures: $1.155 billion, including capital expenditures of $NA (includes West Bank) (2003)
|
|
Agriculture - products:
|


olives, citrus, vegetables; beef, dairy products
|
|
Industries:
|


generally small family businesses that produce textiles, soap, olive-wood carvings, and mother-of-pearl souvenirs; the Israelis have established some small-scale modern industries in an industrial center
|
|
Industrial production growth rate:
|



NA
|
|
Electricity - production:
|



NA kWh; note - electricity supplied by Israel
|
|
Electricity - consumption:
|



NA kWh
|
|
Electricity - exports:
|


0 kWh (2001)
|
|
Electricity - imports:
|


NA kWh; note - electricity supplied by Israel (2001)
|
|
Exports:
|



$603 million f.o.b., includes West Bank
|
|
Exports - commodities:
|


citrus, flowers
|
|
Exports - partners:
|


Israel, Egypt, West Bank
|
|
Imports:
|



$1.9 billion c.i.f., includes West Bank
|
|
Imports - commodities:
|


food, consumer goods, construction materials
|
|
Imports - partners:
|


Israel, Egypt, West Bank
|
|
Debt - external:
|



$108 million (includes West Bank) (1997 est.)
|
|
Economic aid - recipient:
|


$800 million (includes West Bank) (2001 est.)
|
|
Currency:
|


new Israeli shekel (ILS)
|
|
Currency code:
|


ILS
|
|
Exchange rates:
|


new Israeli shekels per US dollar - 4.55 (2003), 4.74 (2002), 4.21 (2001), 4.08 (2000), 4.14 (1999)
|
|
Fiscal year:
|


calendar year
|
This page was last updated on 10 February, 2005
|