


| The World Factbook | ||


|
Poland |

|
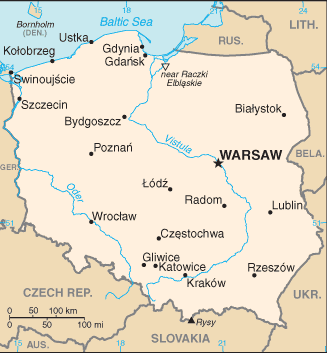
|
| Introduction | Poland |
|
Background:
|
Poland is an ancient nation that was conceived around the middle of the 10th century. Its golden age occurred in the 16th century. During the following century, the strengthening of the gentry and internal disorders weakened the nation. In a series of agreements between 1772 and 1795, Russia, Prussia, and Austria partitioned Poland amongst themselves. Poland regained its independence in 1918 only to be overrun by Germany and the Soviet Union in World War II. It became a Soviet satellite state following the war, but its government was comparatively tolerant and progressive. Labor turmoil in 1980 led to the formation of the independent trade union "Solidarity" that over time became a political force and by 1990 had swept parliamentary elections and the presidency. A "shock therapy" program during the early 1990s enabled the country to transform its economy into one of the most robust in Central Europe, but Poland currently suffers low GDP growth and high unemployment. Solidarity suffered a major defeat in the 2001 parliamentary elections when it failed to elect a single deputy to the lower house of Parliament, and the new leaders of the Solidarity Trade Union subsequently pledged to reduce the Trade Union's political role. Poland joined NATO in 1999 and the European Union in 2004. |
| Geography | Poland |
|
Location:
|
Central Europe, east of Germany |
|
Geographic coordinates:
|
52 00 N, 20 00 E |
|
Map references:
|
Europe |
|
Area:
|
total: 312,685 sq km
water: 8,220 sq km land: 304,465 sq km |
|
Area - comparative:
|
slightly smaller than New Mexico |
|
Land boundaries:
|
total: 2,788 km
border countries: Belarus 407 km, Czech Republic 658 km, Germany 456 km, Lithuania 91 km, Russia (Kaliningrad Oblast) 206 km, Slovakia 444 km, Ukraine 526 km |
|
Coastline:
|
491 km |
|
Maritime claims:
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive economic zone: defined by international treaties |
|
Climate:
|
temperate with cold, cloudy, moderately severe winters with frequent precipitation; mild summers with frequent showers and thundershowers |
|
Terrain:
|
mostly flat plain; mountains along southern border |
|
Elevation extremes:
|
lowest point: near Raczki Elblaskie -2 m
highest point: Rysy 2,499 m |
|
Natural resources:
|
coal, sulfur, copper, natural gas, silver, lead, salt, amber, arable land |
|
Land use:
|
arable land: 45.91%
permanent crops: 1.12% other: 52.97% (2001) |
|
Irrigated land:
|
1,000 sq km (1998 est.) |
|
Natural hazards:
|
flooding |
|
Environment - current issues:
|
situation has improved since 1989 due to decline in heavy industry and increased environmental concern by post-Communist governments; air pollution nonetheless remains serious because of sulfur dioxide emissions from coal-fired power plants, and the resulting acid rain has caused forest damage; water pollution from industrial and municipal sources is also a problem, as is disposal of hazardous wastes; pollution levels should continue to decrease as industrial establishments bring their facilities up to European Union code, but at substantial cost to business and the government |
|
Environment - international agreements:
|
party to: Air Pollution, Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Seals, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Kyoto Protocol, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulfur 94 |
|
Geography - note:
|
historically, an area of conflict because of flat terrain and the lack of natural barriers on the North European Plain |
| People | Poland |
|
Population:
|
38,626,349 (July 2004 est.) |
|
Age structure:
|
0-14 years: 17.1% (male 3,388,247; female 3,216,085)
15-64 years: 70% (male 13,454,820; female 13,591,814) 65 years and over: 12.9% (male 1,896,940; female 3,078,443) (2004 est.) |
|
Median age:
|
total: 36.2 years
male: 34.3 years female: 38.2 years (2004 est.) |
|
Population growth rate:
|
0.02% (2004 est.) |
|
Birth rate:
|
10.64 births/1,000 population (2004 est.) |
|
Death rate:
|
9.97 deaths/1,000 population (2004 est.) |
|
Net migration rate:
|
-0.49 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2004 est.) |
|
Sex ratio:
|
at birth: 1.06 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.05 male(s)/female 15-64 years: 0.99 male(s)/female 65 years and over: 0.62 male(s)/female total population: 0.94 male(s)/female (2004 est.) |
|
Infant mortality rate:
|
total: 8.73 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 7.59 deaths/1,000 live births (2004 est.) male: 9.82 deaths/1,000 live births |
|
Life expectancy at birth:
|
total population: 74.16 years
male: 70.04 years female: 78.52 years (2004 est.) |
|
Total fertility rate:
|
1.38 children born/woman (2004 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:
|
0.1% - note: no country specific models provided (2001 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:
|
14,000 (2003 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - deaths:
|
100 (2001 est.) |
|
Nationality:
|
noun: Pole(s)
adjective: Polish |
|
Ethnic groups:
|
Polish 96.7%, German 0.4%, Belarusian 0.1%, Ukrainian 0.1%, other 2.7% (2002) |
|
Religions:
|
Roman Catholic 95% (about 75% practicing), Eastern Orthodox, Protestant, and other 5% |
|
Languages:
|
Polish |
|
Literacy:
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 99.8% male: 99.8% female: 99.7% (2003 est.) |
| Government | Poland |
|
Country name:
|
conventional long form: Republic of Poland
conventional short form: Poland local short form: Polska local long form: Rzeczpospolita Polska |
|
Government type:
|
republic |
|
Capital:
|
Warsaw |
|
Administrative divisions:
|
16 provinces (wojewodztwa, singular - wojewodztwo); Dolnoslaskie, Kujawsko-Pomorskie, Lodzkie, Lubelskie, Lubuskie, Malopolskie, Mazowieckie, Opolskie, Podkarpackie, Podlaskie, Pomorskie, Slaskie, Swietokrzyskie, Warminsko-Mazurskie, Wielkopolskie, Zachodniopomorskie |
|
Independence:
|
11 November 1918 (independent republic proclaimed) |
|
National holiday:
|
Constitution Day, 3 May (1791) |
|
Constitution:
|
adopted by the National Assembly 2 April 1997; passed by national referendum 25 May 1997; effective 17 October 1997 |
|
Legal system:
|
mixture of Continental (Napoleonic) civil law and holdover Communist legal theory; changes being gradually introduced as part of broader democratization process; limited judicial review of legislative acts, but rulings of the Constitutional Tribunal are final; court decisions can be appealed to the European Court of Justice in Strasbourg |
|
Suffrage:
|
18 years of age; universal |
|
Executive branch:
|
chief of state: President Aleksander KWASNIEWSKI (since 23 December 1995)
elections: president elected by popular vote for a five-year term; election last held 8 October 2000 (next to be held NA October 2005); prime minister and deputy prime ministers appointed by the president and confirmed by the Sejm head of government: Prime Minister Marek BELKA (since 24 June 2004); Deputy Prime Minister Jerzy HAUSNER (since 11 June 2003) cabinet: Council of Ministers responsible to the prime minister and the Sejm; the prime minister proposes, the president appoints, and the Sejm approves the Council of Ministers election results: Aleksander KWASNIEWSKI reelected president; percent of popular vote - Aleksander KWASNIEWSKI 53.9%, Andrzej OLECHOWSKI 17.3%, Marian KRZAKLEWSKI 15.6%, Lech WALESA 1% |
|
Legislative branch:
|
bicameral legislature consisting of an upper house, the Senate or Senat (100 seats; members are elected by a majority vote on a provincial basis to serve four-year terms), and a lower house, the Sejm (460 seats; members are elected under a complex system of proportional representation to serve four-year terms); the designation of National Assembly or Zgromadzenie Narodowe is only used on those rare occasions when the two houses meet jointly
elections: Sejm elections last held 23 September 2001 (next to be held by September 2005); Senate - last held 23 September 2001 (next to be held by September 2005) election results: Sejm - percent of vote by party - SLD-UP 41%, PO 12.7%, Samoobrona 10.2%, PiS 9.5%, PSL 9%, LPR 7.9%, AWSP 5.6% UW 3.1%, other 1%; seats by party (as of 10 December 2004) - SLD 154, PO 56, PiS 44, PSL 40, SDPL 33, SO 30, LPR 25, UP 15, PLD 11, SKL 6, RKN 5, Dom Ojczysty 4, PP 3, ROP 3, German minorities 2, independents 26; Senate - percent of vote by party - NA%; seats by party (as of 10 December 2004)- SLD-UP 74, Block Senate 2001 10, PSL and unaffiliated 5, UW 4, SO 2, LPR 2, independents 2, PiS 1 note: two seats are assigned to ethnic minority parties in the Sejm only |
|
Judicial branch:
|
Supreme Court (judges are appointed by the president on the recommendation of the National Council of the Judiciary for an indefinite period); Constitutional Tribunal (judges are chosen by the Sejm for nine-year terms) |
|
Political parties and leaders:
|
Catholic-National Movement or RKN [Antoni MACIEREWICZ]; Citizens Platform or PO [Donald TUSK]; Coalition Electoral Action Solidarity of the Right or AWSP; Conservative Peasants Party or SKL-RNP [Artur BALAZS]; Democratic Left Alliance or SLD [Krzysztof JANIK]; Freedom Union or UW [Wladyslaw FRASYNIUK]; German Minority of Lower Silesia or MNSO [Henryk KROLL]; Law and Justice or PiS [Jaroslaw KACZYNSKI]; League of Polish Families or LPR [Marek KOTLINOWSKI]; Movement for the Reconstruction of Poland or ROP [Jan OLSZEWSKI]; Peasant-Democratic Party or PLD [Roman JAGIELINSKI]; Polish Accord or PP [Jan LOPUSZANSKI]; Polish Peasant Bloc or PBL [Wojciech MOJZESOWICZ]; Polish Peasant Party or PSL [Janusz WOJCIECHOWSKI]; Polish Raison d'Etat or PRS [Piotr MUSIAL]; Samoobrona or SO [Andrzej LEPPER]; Social Democratic Party of Poland or SDPL [Marek BOROWSKI]; Social Movement or RS [Krzysztof PIESIEWICZ]; Union of Labor or UP [Izabela JARUAGA-NOWACKA] |
|
Political pressure groups and leaders:
|
All Poland Trade Union Alliance or OPZZ (trade union) [Maciej MANICKI]; Roman Catholic Church [Cardinal Jozef GLEMP]; Solidarity Trade Union [Janusz SNIADEK] |
|
International organization participation:
|
ACCT (observer), Australia Group, BIS, BSEC (observer), CBSS, CE, CEI, CERN, EAPC, EBRD, EIB, EU (new member), FAO, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICCt, ICFTU, ICRM, IDA, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, ISO, ITU, MIGA, MINURSO, MONUC, NAM (guest), NATO, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OPCW, OSCE, PCA, PFP, UN, UNCTAD, UNDOF, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNMEE, UNMIK, UNMIL, UNOCI, UNOMIG, UPU, WCL, WCO, WEU (member affiliate), WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WToO, WTO, ZC |
|
Diplomatic representation in the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Przemyslaw GRUDZINSKI
chancery: 2640 16th Street NW, Washington, DC 20009 FAX: [1] (202) 328-6270 consulate(s) general: Chicago, Los Angeles, and New York telephone: [1] (202) 234-3800 through 3802 |
|
Diplomatic representation from the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Victor ASHE
embassy: Aleje Ujazdowskie 29/31 00-540 Warsaw mailing address: American Embassy Warsaw, US Department of State, 5010 Warsaw Place, Washington, DC 20521-5010 (pouch) telephone: [48] (22) 504-2000 FAX: [48] (22) 504-2688 consulate(s) general: Krakow |
|
Flag description:
|
two equal horizontal bands of white (top) and red; similar to the flags of Indonesia and Monaco which are red (top) and white |
| Economy | Poland |
|
Economy - overview:
|
Poland has steadfastly pursued a policy of economic liberalization throughout the 1990s and today stands out as a success story among transition economies. Even so, much remains to be done. The privatization of small and medium state-owned companies and a liberal law on establishing new firms has encouraged the development of the private business sector, but legal and bureaucratic obstacles alongside persistent corruption are hampering its further development. Poland's agricultural sector remains handicapped by structural problems, surplus labor, inefficient small farms, and lack of investment. Restructuring and privatization of "sensitive sectors" (e.g., coal, steel, railroads, and energy), while recently initiated, have stalled. Reforms in health care, education, the pension system, and state administration have resulted in larger than expected fiscal pressures. Further progress in public finance depends mainly on privatization of Poland's remaining state sector, the reduction of state employment, and an overhaul of the tax code to incorporate the growing gray economy and farmers, most of whom pay no tax. The government's determination to enter the EU has shaped most aspects of its economic policy and new legislation; in a nationwide referendum in November 2003, 77% of the voters voted in favor of Poland's EU accession, now scheduled for May 2004. Improving Poland's export competitiveness and containing the internal budget deficit are top priorities. Due to political uncertainty, the zloty has recently depreciated in relation to the euro, while currencies of the other euro-zone aspirants have been appreciating. GDP per capita equals that of the three Baltic states. |
|
GDP:
|
purchasing power parity - $427.1 billion (2003 est.) |
|
GDP - real growth rate:
|
3.7% (2003 est.) |
|
GDP - per capita:
|
purchasing power parity - $11,100 (2003 est.) |
|
GDP - composition by sector:
|
agriculture: 3.1%
industry: 31% services: 65.9% (2003 est.) |
|
Investment (gross fixed):
|
18.4% of GDP (2003) |
|
Population below poverty line:
|
18.4% (2000 est.) |
|
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
|
lowest 10%: 3.2%
highest 10%: 24.7% (1998) |
|
Distribution of family income - Gini index:
|
31.6 (1998) |
|
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
|
0.7% (2003 est.) |
|
Labor force:
|
16.92 million (2003 est.) |
|
Labor force - by occupation:
|
agriculture 27.5%, industry 22.1%, services 50.4% (1999) |
|
Unemployment rate:
|
20% (2003) |
|
Budget:
|
revenues: $39.13 billion
expenditures: $48.64 billion, including capital expenditures of NA (2003) |
|
Public debt:
|
47.4% of GDP (2003) |
|
Agriculture - products:
|
potatoes, fruits, vegetables, wheat; poultry, eggs, pork |
|
Industries:
|
machine building, iron and steel, coal mining, chemicals, shipbuilding, food processing, glass, beverages, textiles |
|
Industrial production growth rate:
|
8.6% (2003) |
|
Electricity - production:
|
135 billion kWh (2001) |
|
Electricity - consumption:
|
118.8 billion kWh (2001) |
|
Electricity - exports:
|
11.04 billion kWh (2001) |
|
Electricity - imports:
|
4.306 billion kWh (2001) |
|
Oil - production:
|
17,180 bbl/day (2001 est.) |
|
Oil - consumption:
|
424,100 bbl/day (2001 est.) |
|
Oil - exports:
|
53,000 bbl/day (2001) |
|
Oil - imports:
|
413,700 bbl/day (2001) |
|
Oil - proved reserves:
|
116.4 million bbl (1 January 2002) |
|
Natural gas - production:
|
5.471 billion cu m (2001 est.) |
|
Natural gas - consumption:
|
13.85 billion cu m (2001 est.) |
|
Natural gas - exports:
|
41 million cu m (2001 est.) |
|
Natural gas - imports:
|
8.782 billion cu m (2001 est.) |
|
Natural gas - proved reserves:
|
154.4 billion cu m (1 January 2002) |
|
Current account balance:
|
$-4.085 billion (2003) |
|
Exports:
|
$57.6 billion f.o.b. (2003 est.) |
|
Exports - commodities:
|
machinery and transport equipment 30.2%, intermediate manufactured goods 25.5%, miscellaneous manufactured goods 20.9%, food and live animals 8.5% (1999) |
|
Exports - partners:
|
Germany 32.3%, France 6.1%, Italy 5.8%, UK 5%, Netherlands 4.5%, Czech Republic 4.1% (2003) |
|
Imports:
|
$63.65 billion f.o.b. (2003 est.) |
|
Imports - commodities:
|
machinery and transport equipment 38.2%, intermediate manufactured goods 20.8%, chemicals 14.3%, miscellaneous manufactured goods 9.5% (1999) |
|
Imports - partners:
|
Germany 24.4%, Italy 8.5%, Russia 7.7%, France 7.1%, China 4.3% (2003) |
|
Reserves of foreign exchange & gold:
|
$33.96 billion (2003) |
|
Debt - external:
|
$86.82 billion (2003) |
|
Economic aid - recipient:
|
EU structural adjustment funds (2000) |
|
Currency:
|
zloty (PLN) |
|
Currency code:
|
PLN |
|
Exchange rates:
|
zlotych per US dollar - 3.8891 (2003), 4.08 (2002), 4.0939 (2001), 4.3461 (2000), 3.9671 (1999)
note: zlotych is the plural form of zloty |
|
Fiscal year:
|
calendar year |
| Communications | Poland |
|
Telephones - main lines in use:
|
12.3 million (2003) |
|
Telephones - mobile cellular:
|
17.4 million (2003) |
|
Telephone system:
|
general assessment: underdeveloped and outmoded system in the process of being overhauled; partial privatization of the state-owned telephone monopoly is underway; the long waiting list for main line telephone service has resulted in a boom in mobile cellular telephone use
domestic: cable, open-wire, and microwave radio relay; 3 cellular networks; local exchanges 56.6% digital international: country code - 48; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat, NA Eutelsat, 2 Inmarsat (Atlantic and Indian Ocean regions), and 1 Intersputnik (Atlantic Ocean region) |
|
Radio broadcast stations:
|
AM 14, FM 777, shortwave 1 (1998) |
|
Radios:
|
20.2 million (1997) |
|
Television broadcast stations:
|
179 (plus 256 repeaters) (September 1995) |
|
Televisions:
|
13.05 million (1997) |
|
Internet country code:
|
.pl |
|
Internet hosts:
|
804,915 (2004) |
|
Internet Service Providers (ISPs):
|
19 (2000) |
|
Internet users:
|
8.97 million (2003) |
| Transportation | Poland |
|
Railways:
|
total: 23,852 km
broad gauge: 629 km 1.524-m gauge standard gauge: 23,223 km 1.435-m gauge (11,962 km electrified) (2003) |
|
Highways:
|
total: 364,656 km
paved: 249,060 km (including 358 km of expressways) unpaved: 115,596 km (2000) |
|
Waterways:
|
3,997 km (navigable rivers and canals) (2003) |
|
Pipelines:
|
gas 13,552 km; oil 1,772 km (2004) |
|
Ports and harbors:
|
Gdansk, Gdynia, Gliwice, Kolobrzeg, Szczecin, Swinoujscie, Ustka, Warsaw, Wroclaw |
|
Merchant marine:
|
total: 14 ships (1,000 GRT or over) 154,710 GRT/228,132 DWT
by type: bulk 7, cargo 3, chemical tanker 3, roll on/roll off 1 registered in other countries: 100 (2004 est.) |
|
Airports:
|
122 (2003 est.) |
|
Airports - with paved runways:
|
total: 84
over 3,047 m: 3 2,438 to 3,047 m: 30 914 to 1,523 m: 8 under 914 m: 3 (2004 est.) 1,524 to 2,437 m: 40 |
|
Airports - with unpaved runways:
|
total: 39
2,438 to 3,047 m: 1 1,524 to 2,437 m: 4 under 914 m: 21 (2004 est.) 914 to 1,523 m: 13 |
|
Heliports:
|
3 (2003 est.) |
| Military | Poland |
|
Military branches:
|
Land Forces, Navy, Air Force |
|
Military manpower - military age and obligation:
|
17 years of age for compulsory military service after January 1st of the year of 18th birthday; 17 years of age for voluntary military service; in 2005 Poland plans to shorten the length of conscript service obligation from 12 to 9 months; by 2008, plans call for at least 60% of military personnel to be volunteers; only soldiers who have completed their conscript service are allowed to volunteer for professional service; as of April 2004 women are only allowed to serve as officers and non-commissioned officers (April 2004) |
|
Military manpower - availability:
|
males age 15-49: 10,291,628 (2004 est.) |
|
Military manpower - fit for military service:
|
males age 15-49: 8,034,577 (2004 est.) |
|
Military manpower - reaching military age annually:
|
males: 329,743 (2004 est.) |
|
Military expenditures - dollar figure:
|
$3.5 billion (2002) |
|
Military expenditures - percent of GDP:
|
1.71% (2002) |
| Transnational Issues | Poland |
|
Disputes - international:
|
none |
|
Illicit drugs:
|
major illicit producer of synthetic drugs for the international market; minor transshipment point for Asian and Latin American illicit drugs to Western Europe |
|
This page was last updated on 10 February, 2005 |