


| The World Factbook | ||


|
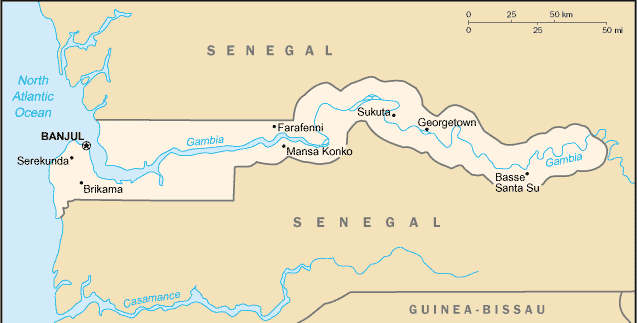
Gambia, The |

|
|
| Introduction | Gambia, The |
|
Background:
|
The Gambia gained its independence from the UK in 1965; it formed a short-lived federation of Senegambia with Senegal between 1982 and 1989. In 1991 the two nations signed a friendship and cooperation treaty. A military coup in 1994 overthrew the president and banned political activity, but a 1996 constitution and presidential elections, followed by parliamentary balloting in 1997, completed a nominal return to civilian rule. The country undertook another round of presidential and legislative elections in late 2001 and early 2002. Yahya A. J. J. JAMMEH, the leader of the coup, has been elected president in all subsequent elections. |
| Geography | Gambia, The |
|
Location:
|
Western Africa, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean and Senegal |
|
Geographic coordinates:
|
13 28 N, 16 34 W |
|
Map references:
|
Africa |
|
Area:
|
total: 11,300 sq km
land: 10,000 sq km water: 1,300 sq km |
|
Area - comparative:
|
slightly less than twice the size of Delaware |
|
Land boundaries:
|
total: 740 km
border countries: Senegal 740 km |
|
Coastline:
|
80 km |
|
Maritime claims:
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive fishing zone: 200 nm contiguous zone: 18 nm continental shelf: not specified |
|
Climate:
|
tropical; hot, rainy season (June to November); cooler, dry season (November to May) |
|
Terrain:
|
flood plain of the Gambia River flanked by some low hills |
|
Elevation extremes:
|
lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
highest point: unnamed location 53 m |
|
Natural resources:
|
fish |
|
Land use:
|
arable land: 25%
permanent crops: 0.5% other: 74.5% (2001) |
|
Irrigated land:
|
20 sq km (1998 est.) |
|
Natural hazards:
|
drought (rainfall has dropped by 30% in the last 30 years) |
|
Environment - current issues:
|
deforestation; desertification; water-borne diseases prevalent |
|
Environment - international agreements:
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
|
Geography - note:
|
almost an enclave of Senegal; smallest country on the continent of Africa |
| People | Gambia, The |
|
Population:
|
1,546,848 (July 2004 est.) |
|
Age structure:
|
0-14 years: 44.7% (male 347,349; female 344,264)
15-64 years: 52.6% (male 403,297; female 410,382) 65 years and over: 2.7% (male 21,459; female 20,097) (2004 est.) |
|
Median age:
|
total: 17.5 years
male: 17.4 years female: 17.7 years (2004 est.) |
|
Population growth rate:
|
2.98% (2004 est.) |
|
Birth rate:
|
40.3 births/1,000 population (2004 est.) |
|
Death rate:
|
12.08 deaths/1,000 population (2004 est.) |
|
Net migration rate:
|
1.57 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2004 est.) |
|
Sex ratio:
|
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.01 male(s)/female 15-64 years: 0.98 male(s)/female 65 years and over: 1.07 male(s)/female total population: 1 male(s)/female (2004 est.) |
|
Infant mortality rate:
|
total: 73.48 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 66.62 deaths/1,000 live births (2004 est.) male: 80.14 deaths/1,000 live births |
|
Life expectancy at birth:
|
total population: 54.79 years
male: 52.76 years female: 56.87 years (2004 est.) |
|
Total fertility rate:
|
5.46 children born/woman (2004 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:
|
1.2% (2003 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:
|
6,800 (2003 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - deaths:
|
600 (2003 est.) |
|
Major infectious diseases:
|
typhoid fever, dengue fever, malaria, yellow fever, Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever, schistosomiasis
overall degree of risk: very high (2004) |
|
Nationality:
|
noun: Gambian(s)
adjective: Gambian |
|
Ethnic groups:
|
African 99% (Mandinka 42%, Fula 18%, Wolof 16%, Jola 10%, Serahuli 9%, other 4%), non-African 1% |
|
Religions:
|
Muslim 90%, Christian 9%, indigenous beliefs 1% |
|
Languages:
|
English (official), Mandinka, Wolof, Fula, other indigenous vernaculars |
|
Literacy:
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 40.1% male: 47.8% female: 32.8% (2003 est.) |
| Government | Gambia, The |
|
Country name:
|
conventional long form: Republic of The Gambia
conventional short form: The Gambia |
|
Government type:
|
republic under multiparty democratic rule |
|
Capital:
|
Banjul |
|
Administrative divisions:
|
5 divisions and 1 city*; Banjul*, Central River, Lower River, North Bank, Upper River, Western |
|
Independence:
|
18 February 1965 (from UK) |
|
National holiday:
|
Independence Day, 18 February (1965) |
|
Constitution:
|
24 April 1970; suspended July 1994; rewritten and approved by national referendum 8 August 1996; reestablished January 1997 |
|
Legal system:
|
based on a composite of English common law, Koranic law, and customary law; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction, with reservations |
|
Suffrage:
|
18 years of age; universal |
|
Executive branch:
|
chief of state: President Yahya A. J. J. JAMMEH (since 18 October 1996; note - from 1994 to 1996 he was Chairman of the Junta); Vice President Isatou Njie SAIDY (since 20 March 1997); note - the president is both the chief of state and head of government
head of government: President Yahya A. J. J. JAMMEH (since 18 October 1996; note - from 1994 to 1996 was he Chairman of the Junta); Vice President Isatou Njie SAIDY (since 20 March 1997); note - the president is both the chief of state and head of government cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president elections: president elected by popular vote for a five-year term; the number of terms is not restricted; election last held 18 October 2001 (next to be held October 2006) election results: Yahya A. J. J. JAMMEH reelected president; percent of vote - Yahya A. J. J. JAMMEH 52.9%, Ousainou DARBOE 32.7% |
|
Legislative branch:
|
unicameral National Assembly (53 seats; 48 elected by popular vote, five appointed by the president; members serve five-year terms)
elections: last held 17 January 2002 (next to be held NA January 2007) election results: percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - APRC 45, PDOIS 2, NRP 1, |
|
Judicial branch:
|
Supreme Court |
|
Political parties and leaders:
|
Alliance for Patriotic Reorientation and Construction or APRC [Yahya A. J. J. JAMMEH]; Gambian People's Party-Progressive People's Party-United Democratic Party or GPP-PPP-UDP Coalition [Ousainou DARBOE]; National Convention Party or NCP [Sheriff DIBBA]; National Reconciliation Party or NRP [Hamat N. K. BAH]; People's Democratic Organization for Independence and Socialism or PDOIS [Sidia JATTA]
note: in August 2001, an independent electoral commission allowed the reregistration of the GPP, NCP, and PPP, three parties banned since 1996 |
|
Political pressure groups and leaders:
|
NA |
|
International organization participation:
|
ACP, AfDB, AU, C, ECOWAS, FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICFTU, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, ITU, MIGA, NAM, OIC, ONUB, OPCW, UN, UNAMSIL, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNMEE, UNMIL, UNOCI, UPU, WCL, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WToO, WTO |
|
Diplomatic representation in the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Lena Manga Sagnia SECK
chancery: Suite 905, 1156 15th Street NW, Washington, DC 20005 FAX: [1] (202) 785-1430 telephone: [1] (202) 785-1379 |
|
Diplomatic representation from the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Jackson McDONALD
embassy: Kairaba Avenue, Fajara, Banjul mailing address: P. M. B. No. 19, Banjul telephone: [220] 392856, 392858, 391971 FAX: [220] 392475 |
|
Flag description:
|
three equal horizontal bands of red (top), blue with white edges, and green |
| Economy | Gambia, The |
|
Economy - overview:
|
The Gambia has no important mineral or other natural resources and has a limited agricultural base. About 75% of the population depends on crops and livestock for its livelihood. Small-scale manufacturing activity features the processing of peanuts, fish, and hides. Reexport trade normally constitutes a major segment of economic activity, but a 1999 government-imposed preshipment inspection plan, and instability of the Gambian dalasi (currency) have drawn some of the reexport trade away from The Gambia. The government's 1998 seizure of the private peanut firm Alimenta eliminated the largest purchaser of Gambian groundnuts; the following two marketing seasons have seen substantially lower prices and sales. A decline in tourism in 2000 has also held back growth. Unemployment and underemployment rates are extremely high. Shortrun economic progress remains highly dependent on sustained bilateral and multilateral aid, on responsible government economic management as forwarded by IMF technical help and advice, and on expected growth in the construction sector. |
|
GDP:
|
purchasing power parity - $2.56 billion (2003 est.) |
|
GDP - real growth rate:
|
3% (2003 est.) |
|
GDP - per capita:
|
purchasing power parity - $1,700 (2003 est.) |
|
GDP - composition by sector:
|
agriculture: 46.8%
industry: 9.3% services: 43.8% (2003 est.) |
|
Investment (gross fixed):
|
20% of GDP (2003) |
|
Population below poverty line:
|
NA |
|
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
|
lowest 10%: NA
highest 10%: NA |
|
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
|
14% (2003 est.) |
|
Labor force:
|
400,000 (1996) |
|
Labor force - by occupation:
|
agriculture 75%, industry, commerce, and services 19%, government 6% |
|
Unemployment rate:
|
NA (2002 est.) |
|
Budget:
|
revenues: $58.63 million
expenditures: $62.64 million, including capital expenditures of $4.1 million (2003 est.) |
|
Agriculture - products:
|
rice, millet, sorghum, peanuts, corn, sesame, cassava (tapioca), palm kernels; cattle, sheep, goats |
|
Industries:
|
processing peanuts, fish, and hides; tourism; beverages; agricultural machinery assembly, woodworking, metalworking; clothing |
|
Industrial production growth rate:
|
NA |
|
Electricity - production:
|
85.33 million kWh (2001) |
|
Electricity - consumption:
|
79.36 million kWh (2001) |
|
Electricity - exports:
|
0 kWh (2001) |
|
Electricity - imports:
|
0 kWh (2001) |
|
Oil - production:
|
0 bbl/day (2001 est.) |
|
Oil - consumption:
|
1,900 bbl/day (2001 est.) |
|
Oil - exports:
|
NA (2001) |
|
Oil - imports:
|
NA (2001) |
|
Current account balance:
|
$-42 million (2003) |
|
Exports:
|
$156 million f.o.b. (2003 est.) |
|
Exports - commodities:
|
peanut products, fish, cotton lint, palm kernels, re-exports |
|
Exports - partners:
|
UK 26.7%, Belgium 6.7%, China 6.7%, Germany 6.7%, Italy 6.7%, Malaysia 6.7%, Thailand 6.7% (2003) |
|
Imports:
|
$271 million f.o.b. (2003 est.) |
|
Imports - commodities:
|
foodstuffs, manufactures, fuel, machinery and transport equipment |
|
Imports - partners:
|
China 24.9%, Senegal 8.9%, Brazil 6.8%, UK 6.6%, US 5.6%, Netherlands 5%, India 4.9% (2003) |
|
Reserves of foreign exchange & gold:
|
$118 million (2003) |
|
Debt - external:
|
$476 million (2001 est.) |
|
Economic aid - recipient:
|
$45.4 million (1995) |
|
Currency:
|
dalasi (GMD) |
|
Currency code:
|
GMD |
|
Exchange rates:
|
dalasi per US dollar - NA (2003), 19.9182 (2002), 15.6872 (2001), 12.7876 (2000), 11.3951 (1999) |
|
Fiscal year:
|
calendar year |
| Communications | Gambia, The |
|
Telephones - main lines in use:
|
38,400 (2002) |
|
Telephones - mobile cellular:
|
100,000 (2002) |
|
Telephone system:
|
general assessment: adequate; a packet switched data network is available
domestic: adequate network of microwave radio relay and open-wire international: country code - 220; microwave radio relay links to Senegal and Guinea-Bissau; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) |
|
Radio broadcast stations:
|
AM 3, FM 2, shortwave 0 (2001) |
|
Radios:
|
196,000 (1997) |
|
Television broadcast stations:
|
1 (government-owned) (1997) |
|
Televisions:
|
5,000 (2000) |
|
Internet country code:
|
.gm |
|
Internet hosts:
|
568 (2004) |
|
Internet Service Providers (ISPs):
|
2 (2001) |
|
Internet users:
|
25,000 (2002) |
| Transportation | Gambia, The |
|
Highways:
|
total: 2,700 km
paved: 956 km unpaved: 1,744 km (1999) |
|
Waterways:
|
390 km (on River Gambia; small ocean-going vessels can reach 190 km) (2004) |
|
Ports and harbors:
|
Banjul |
|
Merchant marine:
|
none (2004 est.) |
|
Airports:
|
1 (2003 est.) |
|
Airports - with paved runways:
|
total: 1
over 3,047 m: 1 (2004 est.) |
| Military | Gambia, The |
|
Military branches:
|
Gambian National Army (GNA) (including Naval Unit), Presidential Guard |
|
Military manpower - military age and obligation:
|
18 years of age for voluntary military service; no conscription (2001) |
|
Military manpower - availability:
|
males age 15-49: 350,256 (2004 est.) |
|
Military manpower - fit for military service:
|
males age 15-49: 176,733 (2004 est.) |
|
Military expenditures - dollar figure:
|
$900,000 (2003) |
|
Military expenditures - percent of GDP:
|
0.3% (2003) |
| Transnational Issues | Gambia, The |
|
Disputes - international:
|
attempts to stem refugees, cross-border raids, arms smuggling, other illegal activities, and political instability from separatist movement in southern Senegal's Casamance region |
|
This page was last updated on 10 February, 2005 |