


| The World Factbook | ||


|
Egypt |

|
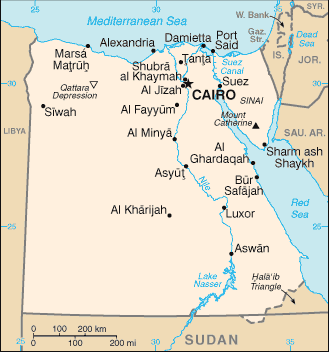
|
| Introduction | Egypt |
|
Background:
|
The regularity and richness of the annual Nile River flood, coupled with semi-isolation provided by deserts to the east and west, allowed for the development of one of the world's great civilizations. A unified kingdom arose circa 3200 B.C. and a series of dynasties ruled in Egypt for the next three millennia. The last native dynasty fell to the Persians in 341 B.C., who in turn were replaced by the Greeks, Romans, and Byzantines. It was the Arabs who introduced Islam and the Arabic language in the 7th century and who ruled for the next six centuries. A local military caste, the Mamluks took control about 1250 and continued to govern after the conquest of Egypt by the Ottoman Turks in 1517. Following the completion of the Suez Canal in 1869, Egypt became an important world transportation hub, but also fell heavily into debt. Ostensibly to protect its investments, Britain seized control of Egypt's government in 1882, but nominal allegiance to the Ottoman Empire continued until 1914. Partially independent from the UK in 1922, Egypt acquired full sovereignty following World War II. The completion of the Aswan High Dam in 1971 and the resultant Lake Nasser have altered the time-honored place of the Nile River in the agriculture and ecology of Egypt. A rapidly growing population (the largest in the Arab world), limited arable land, and dependence on the Nile all continue to overtax resources and stress society. The government has struggled to ready the economy for the new millennium through economic reform and massive investment in communications and physical infrastructure. |
| Geography | Egypt |
|
Location:
|
Northern Africa, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, between Libya and the Gaza Strip, and the Red Sea north of Sudan, and includes the Asian Sinai Peninsula |
|
Geographic coordinates:
|
27 00 N, 30 00 E |
|
Map references:
|
Africa |
|
Area:
|
total: 1,001,450 sq km
land: 995,450 sq km water: 6,000 sq km |
|
Area - comparative:
|
slightly more than three times the size of New Mexico |
|
Land boundaries:
|
total: 2,665 km
border countries: Gaza Strip 11 km, Israel 266 km, Libya 1,115 km, Sudan 1,273 km |
|
Coastline:
|
2,450 km |
|
Maritime claims:
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
continental shelf: 200-m depth or to the depth of exploitation contiguous zone: 24 nm exclusive economic zone: 200 nm |
|
Climate:
|
desert; hot, dry summers with moderate winters |
|
Terrain:
|
vast desert plateau interrupted by Nile valley and delta |
|
Elevation extremes:
|
lowest point: Qattara Depression -133 m
highest point: Mount Catherine 2,629 m |
|
Natural resources:
|
petroleum, natural gas, iron ore, phosphates, manganese, limestone, gypsum, talc, asbestos, lead, zinc |
|
Land use:
|
arable land: 2.87%
permanent crops: 0.48% other: 96.65% (2001) |
|
Irrigated land:
|
33,000 sq km (1998 est.) |
|
Natural hazards:
|
periodic droughts; frequent earthquakes, flash floods, landslides; hot, driving windstorm called khamsin occurs in spring; dust storms, sandstorms |
|
Environment - current issues:
|
agricultural land being lost to urbanization and windblown sands; increasing soil salination below Aswan High Dam; desertification; oil pollution threatening coral reefs, beaches, and marine habitats; other water pollution from agricultural pesticides, raw sewage, and industrial effluents; very limited natural fresh water resources away from the Nile which is the only perennial water source; rapid growth in population overstraining the Nile and natural resources |
|
Environment - international agreements:
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol |
|
Geography - note:
|
controls Sinai Peninsula, only land bridge between Africa and remainder of Eastern Hemisphere; controls Suez Canal, a sea link between Indian Ocean and Mediterranean Sea; size, and juxtaposition to Israel, establish its major role in Middle Eastern geopolitics; dependence on upstream neighbors; dominance of Nile basin issues; prone to influxes of refugees |
| People | Egypt |
|
Population:
|
76,117,421 (July 2004 est.) |
|
Age structure:
|
0-14 years: 33.4% (male 13,038,369; female 12,418,254)
15-64 years: 62.2% (male 23,953,949; female 23,419,418) 65 years and over: 4.3% (male 1,407,248; female 1,880,183) (2004 est.) |
|
Median age:
|
total: 23.4 years
male: 23 years female: 23.8 years (2004 est.) |
|
Population growth rate:
|
1.83% (2004 est.) |
|
Birth rate:
|
23.84 births/1,000 population (2004 est.) |
|
Death rate:
|
5.3 deaths/1,000 population (2004 est.) |
|
Net migration rate:
|
-0.22 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2004 est.) |
|
Sex ratio:
|
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.05 male(s)/female 15-64 years: 1.02 male(s)/female 65 years and over: 0.75 male(s)/female total population: 1.02 male(s)/female (2004 est.) |
|
Infant mortality rate:
|
total: 33.9 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 33.12 deaths/1,000 live births (2004 est.) male: 34.64 deaths/1,000 live births |
|
Life expectancy at birth:
|
total population: 70.71 years
male: 68.22 years female: 73.31 years (2004 est.) |
|
Total fertility rate:
|
2.95 children born/woman (2004 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:
|
less than 0.1% (2001 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:
|
8,000 (2001 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - deaths:
|
700 (2003 est.) |
|
Nationality:
|
noun: Egyptian(s)
adjective: Egyptian |
|
Ethnic groups:
|
Eastern Hamitic stock (Egyptians, Bedouins, and Berbers) 99%, Greek, Nubian, Armenian, other European (primarily Italian and French) 1% |
|
Religions:
|
Muslim (mostly Sunni) 94%, Coptic Christian and other 6% |
|
Languages:
|
Arabic (official), English and French widely understood by educated classes |
|
Literacy:
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 57.7% male: 68.3% female: 46.9% (2003 est.) |
| Government | Egypt |
|
Country name:
|
conventional long form: Arab Republic of Egypt
conventional short form: Egypt local short form: Misr former: United Arab Republic (with Syria) local long form: Jumhuriyat Misr al-Arabiyah |
|
Government type:
|
republic |
|
Capital:
|
Cairo |
|
Administrative divisions:
|
26 governorates (muhafazat, singular - muhafazah); Ad Daqahliyah, Al Bahr al Ahmar, Al Buhayrah, Al Fayyum, Al Gharbiyah, Al Iskandariyah, Al Isma'iliyah, Al Jizah, Al Minufiyah, Al Minya, Al Qahirah, Al Qalyubiyah, Al Wadi al Jadid, Ash Sharqiyah, As Suways, Aswan, Asyut, Bani Suwayf, Bur Sa'id, Dumyat, Janub Sina', Kafr ash Shaykh, Matruh, Qina, Shamal Sina', Suhaj |
|
Independence:
|
28 February 1922 (from UK) |
|
National holiday:
|
Revolution Day, 23 July (1952) |
|
Constitution:
|
11 September 1971 |
|
Legal system:
|
based on English common law, Islamic law, and Napoleonic codes; judicial review by Supreme Court and Council of State (oversees validity of administrative decisions); accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction, with reservations |
|
Suffrage:
|
18 years of age; universal and compulsory |
|
Executive branch:
|
chief of state: President Mohammed Hosni MUBARAK (since 14 October 1981)
head of government: Prime Minister Ahmed NAZIF (since 9 July 2004) cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president elections: president nominated by the People's Assembly for a six-year term, the nomination must then be validated by a national, popular referendum; national referendum last held 26 September 1999 (next to be held NA October 2005); prime minister appointed by the president election results: national referendum validated President MUBARAK's nomination by the People's Assembly to a fourth term |
|
Legislative branch:
|
bicameral system consists of the People's Assembly or Majlis al-Sha'b (454 seats; 444 elected by popular vote, 10 appointed by the president; members serve five-year terms) and the Advisory Council or Majlis al-Shura - which functions only in a consultative role (264 seats; 176 elected by popular vote, 88 appointed by the president; members serve six-year terms)
elections: People's Assembly - three-phase voting - last held 19 October, 29 October, 8 November 2000 (next to be held NA October-November 2005); Advisory Council - last held May-June 2004 (next to be held May-June 2007) election results: People's Assembly - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - NA; Advisory Council - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - NA |
|
Judicial branch:
|
Supreme Constitutional Court |
|
Political parties and leaders:
|
Nasserist Arab Democratic Party or Nasserists [Dia' al-din DAWUD]; National Democratic Party or NDP [President Mohammed Hosni MUBARAK] - governing party; National Progressive Unionist Grouping or Tagammu [Rifaat EL-SAID]; New Wafd Party or NWP [No'man GOMA]; Socialist Liberal Party or Al-Ahrar [Hilmi SALIM]; Tomorrow Party or Al-Ghad [Ayman NOUR]
note: formation of political parties must be approved by the government |
|
Political pressure groups and leaders:
|
despite a constitutional ban against religious-based parties, the technically illegal Muslim Brotherhood constitutes MUBARAK's potentially most significant political opposition; MUBARAK tolerated limited political activity by the Brotherhood for his first two terms, but moved more aggressively since then to block its influence; civic society groups are sanctioned, but constrained in practical terms; trade unions and professional associations are officially sanctioned |
|
International organization participation:
|
ABEDA, ACCT, AfDB, AFESD, AMF, AU, BSEC (observer), CAEU, EBRD, FAO, G-15, G-24, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICCt (signatory), ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, ISO, ITU, LAS, MIGA, MINURSO, MONUC, NAM, OAPEC, OAS (observer), OIC, ONUB, OSCE (partner), PCA, UN, UNAMSIL, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNITAR, UNMIK, UNMIL, UNOMIG, UNRWA, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WToO, WTO |
|
Diplomatic representation in the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador M. Nabil FAHMY
chancery: 3521 International Court NW, Washington, DC 20008 consulate(s) general: Chicago, Houston, New York, and San Francisco FAX: [1] (202) 244-4319 telephone: [1] (202) 895-5400 |
|
Diplomatic representation from the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador C. David WELCH
embassy: 8 Kamal El Din Salah St., Garden City, Cairo mailing address: Unit 64900, Box 15, APO AE 09839-4900 telephone: [20] (2) 797-3300 FAX: [20] (2) 797-3200 |
|
Flag description:
|
three equal horizontal bands of red (top), white, and black; the national emblem (a gold Eagle of Saladin facing the hoist side with a shield superimposed on its chest above a scroll bearing the name of the country in Arabic) centered in the white band; design is based on the Arab Liberation flag and similar to the flag of Syria, which has two green stars, Iraq, which has three green stars (plus an Arabic inscription) in a horizontal line centered in the white band, and Yemen, which has a plain white band |
| Economy | Egypt |
|
Economy - overview:
|
Lack of substantial progress on economic reform since the mid 1990s has limited foreign direct investment in Egypt and kept annual GDP growth in the range of 2-3 percent in 2001-03. Egyptian officials in late 2003 and early 2004 proposed new privatization and customs reform measures, but the government is likely to pursue these initiatives cautiously and gradually to avoid a public backlash over potential inflation or layoffs associated with the reforms. Monetary pressures on an overvalued Egyptian pound led the government to float the currency in January 2003, leading to a sharp drop in its value and consequent inflationary pressure. The existence of a black market for hard currency is evidence that the government continues to influence the official exchange rate offered in banks. In September 2003, Egyptian officials increased subsidies on basic foodstuffs, helping to calm a frustrated public but widening an already deep budget deficit. Egypt's balance-of-payments position was not hurt by the war in Iraq in 2003, as tourism and Suez Canal revenues fared well. The development of an export market for natural gas is a bright spot for future growth prospects, but improvement in the capital-intensive hydrocarbons sector does little to reduce Egypt's persistent unemployment. |
|
GDP:
|
purchasing power parity - $295.2 billion (2003 est.) |
|
GDP - real growth rate:
|
3.1% (2003 est.) |
|
GDP - per capita:
|
purchasing power parity - $4,000 (2003 est.) |
|
GDP - composition by sector:
|
agriculture: 17%
industry: 33% services: 50% (2003) |
|
Investment (gross fixed):
|
16.7% of GDP (2003) |
|
Population below poverty line:
|
16.7% (2000 est.) |
|
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
|
lowest 10%: 3.7%
highest 10%: 29.5% (1999) |
|
Distribution of family income - Gini index:
|
34.4 (1999) |
|
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
|
4.3% (2003 est.) |
|
Labor force:
|
20.19 million (2003 est.) |
|
Labor force - by occupation:
|
agriculture 32%, industry 17%, services 51% (2001 est.) |
|
Unemployment rate:
|
9.9% (2003 est.) |
|
Budget:
|
revenues: $14.69 billion
expenditures: $19.03 billion, including capital expenditures of $2.7 billion (2003) |
|
Public debt:
|
101.8% of GDP (2003) |
|
Agriculture - products:
|
cotton, rice, corn, wheat, beans, fruits, vegetables; cattle, water buffalo, sheep, goats |
|
Industries:
|
textiles, food processing, tourism, chemicals, hydrocarbons, construction, cement, metals |
|
Industrial production growth rate:
|
1.5% (2003 est.) |
|
Electricity - production:
|
75.23 billion kWh (2001) |
|
Electricity - consumption:
|
69.96 billion kWh (2001) |
|
Electricity - exports:
|
0 kWh (2001) |
|
Electricity - imports:
|
0 kWh (2001) |
|
Oil - production:
|
816,900 bbl/day (2001 est.) |
|
Oil - consumption:
|
562,000 bbl/day (2001 est.) |
|
Oil - exports:
|
NA (2001) |
|
Oil - imports:
|
NA (2001) |
|
Oil - proved reserves:
|
3.308 billion bbl (1 January 2002) |
|
Natural gas - production:
|
21.2 billion cu m (2001 est.) |
|
Natural gas - consumption:
|
21.2 billion cu m (2001 est.) |
|
Natural gas - exports:
|
0 cu m (2001 est.) |
|
Natural gas - imports:
|
0 cu m (2001 est.) |
|
Natural gas - proved reserves:
|
1.264 trillion cu m (1 January 2002) |
|
Current account balance:
|
$3.874 billion (2003) |
|
Exports:
|
$8.759 billion f.o.b. (2003 est.) |
|
Exports - commodities:
|
crude oil and petroleum products, cotton, textiles, metal products, chemicals |
|
Exports - partners:
|
US 13.3%, Italy 12.3%, UK 7.9%, France 4.7%, Germany 4.7%, India 4.2% (2003) |
|
Imports:
|
$14.75 billion f.o.b. (2003 est.) |
|
Imports - commodities:
|
machinery and equipment, foodstuffs, chemicals, wood products, fuels |
|
Imports - partners:
|
US 13.6%, Germany 7.4%, Italy 7%, France 6.6%, China 4.8%, Saudi Arabia 4.3% (2003) |
|
Reserves of foreign exchange & gold:
|
$14.22 billion (2003) |
|
Debt - external:
|
$30.34 billion (2003 est.) |
|
Economic aid - recipient:
|
ODA, $1.2 billion (2001) |
|
Currency:
|
Egyptian pound (EGP) |
|
Currency code:
|
EGP |
|
Exchange rates:
|
Egyptian pounds per US dollar - 5.8509 (2003), 4.4997 (2002), 3.973 (2001), 3.4721 (2000), 3.3953 (1999) |
|
Fiscal year:
|
1 July - 30 June |
| Communications | Egypt |
|
Telephones - main lines in use:
|
8,735,700 (2003) |
|
Telephones - mobile cellular:
|
5,797,500 (2003) |
|
Telephone system:
|
general assessment: large system; underwent extensive upgrading during 1990s and is reasonably modern; Internet access and cellular service are available
domestic: principal centers at Alexandria, Cairo, Al Mansurah, Ismailia, Suez, and Tanta are connected by coaxial cable and microwave radio relay international: country code - 20; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean and Indian Ocean), 1 Arabsat, and 1 Inmarsat; 5 coaxial submarine cables; tropospheric scatter to Sudan; microwave radio relay to Israel; a participant in Medarabtel and a signatory to Project Oxygen (a global submarine fiber-optic cable system) |
|
Radio broadcast stations:
|
AM 42 (plus 15 repeaters), FM 14, shortwave 3 (1999) |
|
Radios:
|
20.5 million (1997) |
|
Television broadcast stations:
|
98 (September 1995) |
|
Televisions:
|
7.7 million (1997) |
|
Internet country code:
|
.eg |
|
Internet hosts:
|
3,401 (2004) |
|
Internet Service Providers (ISPs):
|
50 (2000) |
|
Internet users:
|
2.7 million (2003) |
| Transportation | Egypt |
|
Railways:
|
total: 5,063 km
standard gauge: 5,063 km 1.435-m gauge (62 km electrified) (2003) |
|
Highways:
|
total: 64,000 km
paved: 49,984 km unpaved: 14,016 km (1999 est.) |
|
Waterways:
|
3,500 km
note: includes Nile River, Lake Nasser, Alexandria-Cairo Waterway, and numerous smaller canals in delta; Suez Canal (193.5 km including approaches) navigable by oceangoing vessels drawing up to 17.68 m (2004) |
|
Pipelines:
|
condensate 289 km; condensate/gas 94 km; gas 6,115 km; liquid petroleum gas 852 km; oil 5,032 km; oil/gas/water 36 km; refined products 246 km (2004) |
|
Ports and harbors:
|
Alexandria, Al Ghardaqah, Aswan, Asyut, Bur Safajah, Damietta, Marsa Matruh, Port Said, Suez |
|
Merchant marine:
|
total: 159 ships (1,000 GRT or over) 1,194,696 GRT/1,754,815 DWT
foreign-owned: China 2, Cyprus 1, Denmark 1, Greece 6, Lebanon 2, Turkey 1 registered in other countries: 50 (2004 est.) by type: bulk 18, cargo 41, container 5, passenger 64, petroleum tanker 14, roll on/roll off 13, short-sea/passenger 4 |
|
Airports:
|
89 (2003 est.) |
|
Airports - with paved runways:
|
total: 72
over 3,047 m: 13 2,438 to 3,047 m: 38 under 914 m: 4 (2004 est.) 1,524 to 2,437 m: 17 |
|
Airports - with unpaved runways:
|
total: 15
under 914 m: 7 (2004 est.) 2,438 to 3,047 m: 1 1,524 to 2,437 m: 2 914 to 1,523 m: 5 |
|
Heliports:
|
2 (2003 est.) |
| Military | Egypt |
|
Military branches:
|
Army, Navy, Air Force, Air Defense Command |
|
Military manpower - military age and obligation:
|
18 years of age for conscript military service; 3-year service obligation (2001) |
|
Military manpower - availability:
|
males age 15-49: 20,340,716 (2004 est.) |
|
Military manpower - fit for military service:
|
males age 15-49: 13,148,944 (2004 est.) |
|
Military manpower - reaching military age annually:
|
males: 756,233 (2004 est.) |
|
Military expenditures - dollar figure:
|
$2,443.2 million (2003) |
|
Military expenditures - percent of GDP:
|
3.6% (2003) |
| Transnational Issues | Egypt |
|
Disputes - international:
|
Egypt and Sudan retain claims to administer the triangular areas that extend north and south of the 1899 Treaty boundary along the 22nd Parallel, but have withdrawn their military presence; Egypt is economically developing and effectively administers the "Hala'ib Triangle" north of the Treaty line |
|
Refugees and internally displaced persons:
|
refugees (country of origin): 70,215 (Palestinian Territories) (2004) |
|
Illicit drugs:
|
transit point for Southwest Asian and Southeast Asian heroin and opium moving to Europe, Africa, and the US; transit stop for Nigerian couriers; concern as money-laundering site due to lax financial regulations and enforcement |
|
This page was last updated on 10 February, 2005 |