


| The World Factbook | ||


|
Afghanistan |

|
|
| Introduction | Afghanistan |
|
Background:
|
Afghanistan's recent history is a story of war and civil unrest. The Soviet Union invaded in 1979, but was forced to withdraw 10 years later by anti-Communist mujahidin forces. The Communist regime in Kabul collapsed in 1992. Fighting that subsequently erupted among the various mujahidin factions eventually helped to spawn the Taliban, a hardline Pakistani-sponsored movement that fought to end the warlordism and civil war which gripped the country. The Taliban seized Kabul in 1996 and were able to capture most of the country outside of Northern Alliance srongholds primarily in the northeast. Following the 11 September 2001 terrorist attacks, a US, Allied, and Northern Alliance military action toppled the Taliban for sheltering Osama BIN LADIN. In late 2001, a conference in Bonn, Germany, established a process for political reconstruction that ultimately resulted in the adoption of a new constitution and presidential election in 2004. On 9 October 2004, Hamid KARZAI became the first democratically elected president of Afghanistan. The new Afghan government's next task is to hold National Assembly elections, tentatively scheduled for April 2005. |
| Geography | Afghanistan |
|
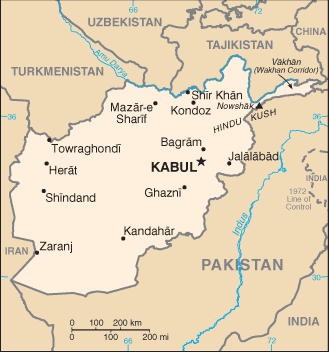
Location:
|
Southern Asia, north and west of Pakistan, east of Iran |
|
Geographic coordinates:
|
33 00 N, 65 00 E |
|
Map references:
|
Asia |
|
Area:
|
total: 647,500 sq km
water: 0 sq km land: 647,500 sq km |
|
Area - comparative:
|
slightly smaller than Texas |
|
Land boundaries:
|
total: 5,529 km
border countries: China 76 km, Iran 936 km, Pakistan 2,430 km, Tajikistan 1,206 km, Turkmenistan 744 km, Uzbekistan 137 km |
|
Coastline:
|
0 km (landlocked) |
|
Maritime claims:
|
none (landlocked) |
|
Climate:
|
arid to semiarid; cold winters and hot summers |
|
Terrain:
|
mostly rugged mountains; plains in north and southwest |
|
Elevation extremes:
|
lowest point: Amu Darya 258 m
highest point: Nowshak 7,485 m |
|
Natural resources:
|
natural gas, petroleum, coal, copper, chromite, talc, barites, sulfur, lead, zinc, iron ore, salt, precious and semiprecious stones |
|
Land use:
|
arable land: 12.13%
permanent crops: 0.22% other: 87.65% (2001) |
|
Irrigated land:
|
23,860 sq km (1998 est.) |
|
Natural hazards:
|
damaging earthquakes occur in Hindu Kush mountains; flooding; droughts |
|
Environment - current issues:
|
limited natural fresh water resources; inadequate supplies of potable water; soil degradation; overgrazing; deforestation (much of the remaining forests are being cut down for fuel and building materials); desertification; air and water pollution |
|
Environment - international agreements:
|
party to: Biodiversity, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Marine Dumping
signed, but not ratified: Climate Change, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Life Conservation |
|
Geography - note:
|
landlocked; the Hindu Kush mountains that run northeast to southwest divide the northern provinces from the rest of the country; the highest peaks are in the northern Vakhan (Wakhan Corridor) |
| People | Afghanistan |
|
Population:
|
28,513,677 (July 2004 est.) |
|
Age structure:
|
0-14 years: 44.7% (male 6,525,929; female 6,222,497)
15-64 years: 52.9% (male 7,733,707; female 7,346,226) 65 years and over: 2.4% (male 334,427; female 350,891) (2004 est.) |
|
Median age:
|
total: 17.5 years
male: 17.5 years female: 17.6 years (2004 est.) |
|
Population growth rate:
|
4.92%
note: this rate does not take into consideration the recent war and its continuing impact (2004 est.) |
|
Birth rate:
|
47.27 births/1,000 population (2004 est.) |
|
Death rate:
|
21.12 deaths/1,000 population (2004 est.) |
|
Net migration rate:
|
23.06 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2004 est.) |
|
Sex ratio:
|
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.05 male(s)/female 15-64 years: 1.05 male(s)/female 65 years and over: 0.95 male(s)/female total population: 1.05 male(s)/female (2004 est.) |
|
Infant mortality rate:
|
total: 165.96 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 160.82 deaths/1,000 live births (2004 est.) male: 170.85 deaths/1,000 live births |
|
Life expectancy at birth:
|
total population: 42.46 years
male: 42.27 years female: 42.66 years (2004 est.) |
|
Total fertility rate:
|
6.78 children born/woman (2004 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:
|
0.01% (2001 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:
|
NA |
|
HIV/AIDS - deaths:
|
NA |
|
Nationality:
|
noun: Afghan(s)
adjective: Afghan |
|
Ethnic groups:
|
Pashtun 42%, Tajik 27%, Hazara 9%, Uzbek 9%, Aimak 4%, Turkmen 3%, Baloch 2%, other 4% |
|
Religions:
|
Sunni Muslim 80%, Shi'a Muslim 19%, other 1% |
|
Languages:
|
Pashtu (official) 35%, Afghan Persian (Dari) 50%, Turkic languages (primarily Uzbek and Turkmen) 11%, 30 minor languages (primarily Balochi and Pashai) 4%, much bilingualism |
|
Literacy:
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
female: 21% (1999 est.) total population: 36% male: 51% |
|
People - note:
|
of the estimated 4 million refugees in October 2001, 2.3 million have returned |
| Government | Afghanistan |
|
Country name:
|
conventional long form: Islamic Republic of Afghanistan
conventional short form: Afghanistan local short form: Afghanestan former: Republic of Afghanistan local long form: Dowlat-e Eslami-ye Afghanestan |
|
Government type:
|
Islamic republic |
|
Capital:
|
Kabul |
|
Administrative divisions:
|
34 provinces (velayat, singular - velayat); Badakhshan, Badghis, Baghlan, Balkh, Bamian, Daykondi, Farah, Faryab, Ghazni, Ghowr, Helmand, Herat, Jowzjan, Kabol, Kandahar, Kapisa, Khowst, Konar, Kondoz, Laghman, Lowgar, Nangarhar, Nimruz, Nurestan, Oruzgan, Paktia, Paktika, Panjshir, Parvan, Samangan, Sar-e Pol, Takhar, Vardak, and Zabol |
|
Independence:
|
19 August 1919 (from UK control over Afghan foreign affairs) |
|
National holiday:
|
Independence Day, 19 August (1919) |
|
Constitution:
|
new constitution drafted 14 December 2003 - 4 January 2004; signed 16 January 2004 |
|
Legal system:
|
according to the new constitution, no law should be "contrary to Islam"; the state is obliged to create a prosperous and progressive society based on social justice, protection of human dignity, protection of human rights, realization of democracy, and to ensure national unity and equality among all ethnic groups and tribes; the state shall abide by the UN charter, international treaties, international conventions that Afghanistan signed, and the Universal Declaration of Human Rights |
|
Suffrage:
|
18 years of age; universal |
|
Executive branch:
|
chief of state: President of the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, Hamid KARZAI (since 7 December 2004); note - the president is both the chief of state and head of government; former King ZAHIR Shah holds the honorific, "Father of the Country," and presides symbolically over certain occasions, but lacks any governing authority; the honorific is not hereditary
head of government: President of the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, Hamid KARZAI (since 7 December 2004); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government cabinet: 27 ministers; note - under the new constitution, ministers are appointed by the president and approved by the National Assembly elections: the president and two vice presidents are elected by direct vote for a five-year term; if no candidate receives 50% or more of the vote in the first round of voting, the two candidates with the most votes will participate in a second round; a president can only be elected for two terms; election last held 9 October 2004 (next to be held in 2009) election results: Hamid KARZAI elected president; percent of vote - Hamid KARZAI - 55.4%, Yunus QANOONI - 16.3%, Mohammad MOHAQEQ - 11.6%, Abdul Rashid DOSTAM 10.0%, Abdul Latif PEDRAM - 1.4%, Masooda JALAL - 1.2% |
|
Legislative branch:
|
nonfunctioning as of January 2004; government is empowered by the constitution to issue legislation by decree until the new assembly is seated; under the new constitution, the bicameral National Assembly will consist of the Wolesi Jirga or House of People (no more than 249 seats), directly elected for a five-year term, and the Meshrano Jirga or House of Elders (102 seats, one third elected from provincial councils for a four-year term, one third elected from local district councils for a three-year term, and one third presidential appointees for a five-year term; the presidential appointees will include two representatives of Kuchis and two representatives of the disabled; half of the presidential appointees will be women)
note: on rare occasions the government may convene the Loya Jirga on issues of independence, national sovereignty, and territorial integrity; it can amend the provisions of the constitution and prosecute the president; it is made up of members of the National Assembly and chairpersons of the provincial and district councils elections: scheduled for spring 2005 |
|
Judicial branch:
|
the new constitution establishes a nine-member Stera Mahkama or Supreme Court (its nine justices are appointed for 10-year terms by the president with approval of the Wolesi Jirga) and subordinate High Courts and Appeals Courts; there is also a Minister of Justice; a separate Afghan Independent Human Rights Commission established by the Bonn Agreement is charged with investigating human rights abuses and war crimes |
|
Political parties and leaders:
|
note - includes only political parties approved by the Ministry of Justice: Afghan Millat [Anwarul Haq AHADI]; De Afghanistan De Solay Ghorzang Gond [Shahnawaz TANAI]; De Afghanistan De Solay Mili Islami Gond [Shah Mahmood Polal ZAI]; Harakat-e-Islami Afghanistan [Mohammad Asif MOHSINEE]; Hezb-e-Aarman-e-Mardum-e-Afghanistan [Iihaj Saraj-u-din ZAFAREE]; Hezb-e-Aazadee Afghanistan [Abdul MALIK]; Hezb-e-Adalat-e-Islami Afghanistan [Mohammad Kabeer MARZBAN]; Hezb-e-Afghanistan-e-Wahid [Mohammad Wasil RAHEEMEE]; Hezb-e-Afghan Watan Islami Gond [NA leader]; Hezb-e-Congra-e-Mili Afghanistan [Lateef PIDRAM]; Hezb-e-Falah-e-Mardum-e-Afghanistan [Mohammad ZAREEF]; Hezb-e-Libral-e-Aazadee Khwa-e-Mardum-e-Afghanistan [Ajmal SOHAIL]; Hezb-e-Hambastagee Mili Jawanan-e-Afghanistan [Mohammad Jamil KARZAI]; Hezb-e-Hamnbatagee-e-Afghanistan [Abdul Khaleq NEMAT]; Hezb-e-Harakat-e-Mili Wahdat-e-Afghanistan [Moahammad Nadir AATASH]; Hezb-e-Harak-e-Islami Mardum-e-Afghanistan [Ilhaj Said Hssain ANWARY]; Hezb-e-Ifazat Az Uqoq-e-Bashar Wa Inkishaf-e-Afghanistan [Baryalai NASRATEE]; Hezb-e-Istiqlal-e-Afghanistan [Dr. Gh. Farooq NIJZRABEE]; Hezb-e-Jamhoree Khwahan [Sibghatullah SANJAR]; Hezb-e-Kar Wa Tawsiha-e-Afghanistan [Zulfiar OMID]; Hezb-e-Mili Afghanistan [Abdul Rasheed AARYAN]; Hezb-e-Mili Wahdat-e-Aqwam-e-Islami Afghanistan [Mohammad Shah KHOGYANEE]; Hezb-e-Nuhzhat-e-Mili Afghanistan [Ahmad Wali MASOUD]; Hezb-e-Paiwand-e-Mili Afghanistan [Said Mansoor NADIRI]; Hezb-e-Rastakhaiz-e-Islami Mardum-e-Afghanistan [Said ZAHIR]; Hezb-e-Refah-e-Mardum-e-Afghanistan [Mia Gul WASEEQ]; Hezb-e-Risalat-e-Mardum-e-Afghanistan [Noor Aqa ROEEN]; Hezb-e-Sahadat-e-Mardum-e-Afghanistan [Mohammad Zubair PAIROZ]; Hezb-e-Sahadat-e-Mili Wa Islami Afghanistan [Mohammad Usman SALIGZADA]; Hezb-e-Sulh-e-Mili Islami Aqwam-e-Afghanistan [Abdul Qahir SHARYATEE]; Hezb-e-Sulh Wa Wahdat-e-Mili Afghanistan [Abdul Qadir IMAMEE]; Hezb-e-Tafahum-e-Wa Democracy Afghanistan [Ahamad SHAHEEN]; Hezb-e-Wahdat-e-Islami Afghanistan [Mohammad Karim KHALILI]; Hezb-e-Wahdat-e-Islami Mardum-e-Afghanistan [Haji Mohammad MUHAQIQ]; Hezb-e-Wahdat-e-Mili Afghanistan [Abdul Rasheed Jalili]; Jamahat-ul-Dahwat ilal Qurhan-wa-Sunat-ul-Afghanistan [Mawlawee Samiullah NAJEEBEE]; Jombesh-e Milli [Abdul Rashjid DOSTUM]; Mahaz-e-Mili Islami Afghanistan [Said Ahmad GAILANEE]; Majmah-e-Mili Fahaleen-e-Sulh-e-Afghanistan [Shams ul Haq Noor SHAMS]; Nuhzat-e-Aazadee Wa democracy Afghanistan [Abdul Raqeeb Jawid KUHISTANEE]; Nuhzat-e-Hambastagee Mili Afghanistan [Peer Said Ishaq GAILANEE]; Sazman-e-Islami Afghanistan-e-Jawan [Siad Jawad HUSSAINEE]; Tahreek Wahdat-e-Mili [Sultan Mahmood DHAZI] (30 Sep 2004) |
|
Political pressure groups and leaders:
|
Jamiat-e Islami (Society of Islam), [former President Burhanuddin RABBANI]; Ittihad-e Islami (Islamic Union for the Liberation of Afghanistan), [Abdul Rasul SAYYAF]; there are also small monarchist, communist, and democratic groups |
|
International organization participation:
|
AsDB, CP, ECO, FAO, G-77, GUUAM, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, Interpol, IOC, IOM, ITU, MIGA, NAM, NATO, OIC, OPCW, OSCE, SACEP, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WMO, WTO (observer), WToO |
|
Diplomatic representation in the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Said Tayeb JAWAD
consulate(s) general: New York FAX: [1] 202-483-6488 telephone: [1] 202-483-6410 chancery: 2118 Kalorama Road NW, Washington, DC 20008 |
|
Diplomatic representation from the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Zalmay KHALILZAD
embassy: The Great Masood Road, Kabul mailing address: 6180 Kabul Place, Dulles, VA 20189-6180 telephone: [00] (2) 230-0436 FAX: [0093] (2) 230-1364 |
|
Flag description:
|
three equal vertical bands of black (hoist), red, and green, with a gold emblem centered on the red band; the emblem features a temple-like structure encircled by a wreath on the left and right and by a bold Islamic inscription above |
| Economy | Afghanistan |
|
Economy - overview:
|
Afghanistan's economic outlook has improved significantly over the past two years because of the infusion of over $2 billion in international assistance, dramatic improvements in agricultural production, and the end of a four-year drought in most of the country. However, Afghanistan remains extremely poor, landlocked, and highly dependent on foreign aid, farming, and trade with neighboring countries. It will probably take the remainder of the decade and continuing donor aid and attention to raise Afghanistan's living standards up from its current status among the lowest in the world. Much of the population continues to suffer from shortages of housing, clean water, electricity, medical care, and jobs, but the Afghan government and international donors remain committed to improving access to these basic necessities by prioritizing infrastructure development, education, housing development, jobs programs, and economic reform over the next year. Growing political stability and continued international commitment to Afghan reconstruction create an optimistic outlook for maintaining improvements to the Afghan economy in 2004. The replacement of the opium trade - which may account for one-third of GDP - is one of several potential spoilers for the economy over the long term. |
|
GDP:
|
purchasing power parity - $20 billion (2003 est.) |
|
GDP - real growth rate:
|
29% (2003 est.)
: note: this high growth rate reflects the extremely low levels of activity between 1999 and 2002, as well as the end of a four-year drought and the impact of donor assistance |
|
GDP - per capita:
|
purchasing power parity - $700 (2003 est.) |
|
GDP - composition by sector:
|
agriculture: 60%
industry: 20% services: 20% (1990 est.) |
|
Population below poverty line:
|
23% (2002) |
|
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
|
lowest 10%: NA
highest 10%: NA |
|
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
|
5.2% (2003) |
|
Labor force:
|
11.8 million (2001 est.) |
|
Labor force - by occupation:
|
agriculture 80%, industry 10%, services 10% (1990 est.) |
|
Unemployment rate:
|
NA (2003) |
|
Budget:
|
revenues: $200 million
expenditures: $550 million, including capital expenditures of NA (2003 plan) |
|
Agriculture - products:
|
opium, wheat, fruits, nuts, wool, mutton, sheepskins, lambskins |
|
Industries:
|
small-scale production of textiles, soap, furniture, shoes, fertilizer, cement; handwoven carpets; natural gas, coal, copper |
|
Industrial production growth rate:
|
NA |
|
Electricity - production:
|
334.8 million kWh (2001) |
|
Electricity - consumption:
|
511.4 million kWh (2001) |
|
Electricity - exports:
|
0 kWh (2001) |
|
Electricity - imports:
|
200 million kWh (2001) |
|
Oil - production:
|
0 bbl/day (2001 est.) |
|
Oil - consumption:
|
3,500 bbl/day (2001 est.) |
|
Oil - exports:
|
NA (2001) |
|
Oil - imports:
|
NA (2001) |
|
Oil - proved reserves:
|
0 bbl (1 January 2002) |
|
Natural gas - production:
|
220 million cu m (2001 est.) |
|
Natural gas - consumption:
|
220 million cu m (2001 est.) |
|
Natural gas - exports:
|
0 cu m (2001 est.) |
|
Natural gas - imports:
|
0 cu m (2001 est.) |
|
Natural gas - proved reserves:
|
49.98 billion cu m (1 January 2002) |
|
Exports:
|
$98 million (not including illicit exports) (2002 est.) |
|
Exports - commodities:
|
opium, fruits and nuts, handwoven carpets, wool, cotton, hides and pelts, precious and semi-precious gems |
|
Exports - partners:
|
US 27%, France 17.5%, India 16.6%, Pakistan 13.3% (2003) |
|
Imports:
|
$1.007 billion (2002 est.) |
|
Imports - commodities:
|
capital goods, food, textiles, petroleum products |
|
Imports - partners:
|
Pakistan 30.1%, South Korea 9.2%, Japan 7.6%, Germany 6.9%, Turkmenistan 5.4%, Kenya 4.6%, US 4.5%, Russia 4% (2003) |
|
Debt - external:
|
$8 billion in bilateral debt, mostly to Russia; Afghanistan has $500 million in debt to Multilateral Development Banks (2004) |
|
Economic aid - recipient:
|
international pledges made by more than 60 countries and international financial institutions at the Tokyo Donors Conference for Afghan reconstruction in January 2002 reached $4.5 billion through 2006, with $1.8 billion allocated for 2002; another $1.7 billion was pledged for 2003. |
|
Currency:
|
afghani (AFA) |
|
Currency code:
|
AFA |
|
Exchange rates:
|
afghanis per US dollar - 50 (2003), 50 (2002), 3,000 (2001), 3,000 (2000), 3,000 (1999)
: note: in 2002, the afghani was revalued and the currency stabilized at about 50 afghanis to the dollar; before 2002, the market rate varied widely from the official rate |
|
Fiscal year:
|
21 March - 20 March |
| Communications | Afghanistan |
|
Telephones - main lines in use:
|
33,100 (2002) |
|
Telephones - mobile cellular:
|
15,000 (2002) |
|
Telephone system:
|
general assessment: very limited telephone and telegraph service
domestic: telephone service is improving with the establishment of two mobile phone operators by 2003; telephone main lines remain weak with only .1 line per 10 people international: country code - 93; five VSAT's installed in Kabul, Herat, Mazar-e-Sharif, Kandahar, and Jalalabad provide international and domestic voice and data connectivity |
|
Radio broadcast stations:
|
AM 21, FM 23, shortwave 1 (broadcasts in Pashtu, Afghan Persian (Dari), Urdu, and English) (2003) |
|
Radios:
|
167,000 (1999) |
|
Television broadcast stations:
|
at least 10 (one government-run central television station in Kabul and regional stations in nine of the 32 provinces; the regional stations operate on a reduced schedule; also, in 1997, there was a station in Mazar-e Sharif reaching four northern Afghanistan provinces) (1998) |
|
Televisions:
|
100,000 (1999) |
|
Internet country code:
|
.af |
|
Internet Service Providers (ISPs):
|
1 (2000) |
|
Internet users:
|
1,000 (2002) |
|
Communications - note:
|
in March 2003 'af' was established as Afghanistan's domain name; Internet access is growing through Internet cafes as well as public "telekiosks" in Kabul that are part of a nationwide network proposed by the Transitional Authority for Internet access (2002) |
| Transportation | Afghanistan |
|
Highways:
|
total: 21,000 km
paved: 2,793 km unpaved: 18,207 km (1999 est.) |
|
Waterways:
|
1,200 km
note: chiefly Amu Darya, which handles vessels up to 500 DWT (2004) |
|
Pipelines:
|
gas 387 km (2004) |
|
Ports and harbors:
|
Kheyrabad, Shir Khan |
|
Airports:
|
47 (2003 est.) |
|
Airports - with paved runways:
|
total: 10
over 3,047 m: 3 2,438 to 3,047 m: 4 under 914 m: 1 (2004 est.) 1,524 to 2,437 m: 2 |
|
Airports - with unpaved runways:
|
total: 37
under 914 m: 11 (2004 est.) 914 to 1,523 m: 4 over 3,047 m: 1 2,438 to 3,047 m: 7 1,524 to 2,437 m: 14 |
|
Heliports:
|
5 (2003 est.) |
| Military | Afghanistan |
|
Military branches:
|
Afghan National Army, currently being trained by the US with the assistance of the international community, is 7,000 strong; note - the December 2001 Bonn Agreement called for all militia forces to come under the authority of the central government, but regional leaders have continued to retain their militias and the formation of a national army remains a gradual process; Afghanistan's militia forces continue to be factionalized, largely along ethnic lines |
|
Military manpower - military age and obligation:
|
22 years of age (2004 est.) |
|
Military manpower - availability:
|
males age 15-49: 6,785,414 (2004 est.) |
|
Military manpower - fit for military service:
|
males age 15-49: 3,642,659 (2004 est.) |
|
Military manpower - reaching military age annually:
|
males: 263,406 (2004 est.) |
|
Military expenditures - dollar figure:
|
$61 million (2003) |
|
Military expenditures - percent of GDP:
|
1% (2003) |
| Transnational Issues | Afghanistan |
|
Disputes - international:
|
despite largely successful UN efforts at voluntary repatriation, 2-3 million Afghan refugees continue to reside in Iran and Pakistan, many at their own choosing; Pakistan has sent troops into remote tribal areas to control the border and stem organized terrorist and other illegal cross-border activites; regular meetings between Pakistani and coalition allies aim to resolve periodic claims of boundary encroachments; occasional conflicts over water-sharing arrangements with Amu Darya and Helmand River states |
|
Refugees and internally displaced persons:
|
IDPs: 167,000 - 200,000 (mostly Pashtuns and Kuchis displaced in south and west due to drought and instability) (2004) |
|
Illicit drugs:
|
world's largest producer of opium; cultivation of opium poppy reached unprecedented level of 206,700 hectares in 2004; counterdrug efforts largely unsuccessful; potential opium production of 4,950 metric tons; potential heroin production of 582 metric tons if all opium was processed; source of hashish; many narcotics-processing labs throughout the country; drug trade source of instability and some antigovernment groups profit from the trade; 80-90% of the heroin consumed in Europe comes from Afghan opium; vulnerable to narcotics money laundering through informal financial networks |
|
This page was last updated on 10 February, 2005 |