


| The World Factbook | ||


|
Thailand |

|
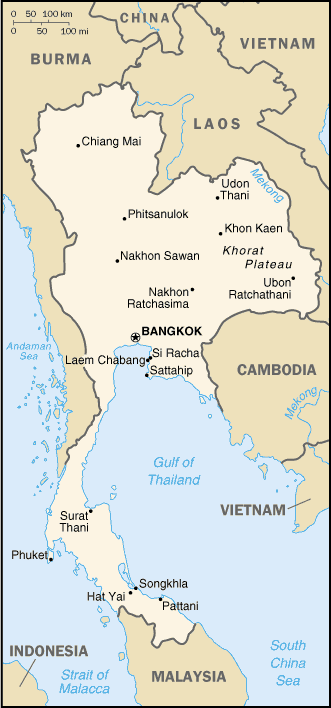
|
| Introduction | Thailand |
|
Background:
|
A unified Thai kingdom was established in the mid-14th century. Known as Siam until 1939, Thailand is the only Southeast Asian country never to have been taken over by a European power. A bloodless revolution in 1932 led to a constitutional monarchy. In alliance with Japan during World War II, Thailand became a US ally following the conflict. |
| Geography | Thailand |
|
Location:
|
Southeastern Asia, bordering the Andaman Sea and the Gulf of Thailand, southeast of Burma |
|
Geographic coordinates:
|
15 00 N, 100 00 E |
|
Map references:
|
Southeast Asia |
|
Area:
|
total: 514,000 sq km
water: 2,230 sq km land: 511,770 sq km |
|
Area - comparative:
|
slightly more than twice the size of Wyoming |
|
Land boundaries:
|
total: 4,863 km
border countries: Burma 1,800 km, Cambodia 803 km, Laos 1,754 km, Malaysia 506 km |
|
Coastline:
|
3,219 km |
|
Maritime claims:
|
continental shelf: 200-m depth or to the depth of exploitation
exclusive economic zone: 200 NM territorial sea: 12 NM |
|
Climate:
|
tropical; rainy, warm, cloudy southwest monsoon (mid-May to September); dry, cool northeast monsoon (November to mid-March); southern isthmus always hot and humid |
|
Terrain:
|
central plain; Khorat Plateau in the east; mountains elsewhere |
|
Elevation extremes:
|
lowest point: Gulf of Thailand 0 m
highest point: Doi Inthanon 2,576 m |
|
Natural resources:
|
tin, rubber, natural gas, tungsten, tantalum, timber, lead, fish, gypsum, lignite, fluorite, arable land |
|
Land use:
|
arable land: 32.88%
permanent crops: 7% other: 60.12% (1998 est.) |
|
Irrigated land:
|
47,490 sq km (1998 est.) |
|
Natural hazards:
|
land subsidence in Bangkok area resulting from the depletion of the water table; droughts |
|
Environment - current issues:
|
air pollution from vehicle emissions; water pollution from organic and factory wastes; deforestation; soil erosion; wildlife populations threatened by illegal hunting |
|
Environment - international agreements:
|
party to: Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Marine Life Conservation, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: Biodiversity, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Law of the Sea |
|
Geography - note:
|
controls only land route from Asia to Malaysia and Singapore |
| People | Thailand |
|
Population:
|
64,265,276
note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality and death rates, lower population and growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected (July 2003 est.) |
|
Age structure:
|
0-14 years: 24.2% (male 7,955,597; female 7,604,652)
15-64 years: 68.8% (male 21,819,445; female 22,362,085) 65 years and over: 7% (male 2,081,768; female 2,441,729) (2003 est.) |
|
Median age:
|
total: 30.1 years
male: 29.4 years female: 30.8 years (2002) |
|
Population growth rate:
|
0.95% (2003 est.) |
|
Birth rate:
|
16.37 births/1,000 population (2003 est.) |
|
Death rate:
|
6.86 deaths/1,000 population (2003 est.) |
|
Net migration rate:
|
0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2003 est.) |
|
Sex ratio:
|
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.05 male(s)/female 15-64 years: 0.98 male(s)/female 65 years and over: 0.85 male(s)/female total population: 0.98 male(s)/female (2003 est.) |
|
Infant mortality rate:
|
total: 21.83 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 20.41 deaths/1,000 live births (2003 est.) male: 23.17 deaths/1,000 live births |
|
Life expectancy at birth:
|
total population: 71.24 years
male: 69.07 years female: 73.53 years (2003 est.) |
|
Total fertility rate:
|
1.91 children born/woman (2003 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:
|
1.8% (2001 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:
|
670,000 (2001 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - deaths:
|
55,000 (2001 est.) |
|
Nationality:
|
noun: Thai (singular and plural)
adjective: Thai |
|
Ethnic groups:
|
Thai 75%, Chinese 14%, other 11% |
|
Religions:
|
Buddhism 95%, Muslim 3.8%, Christianity 0.5%, Hinduism 0.1%, other 0.6% (1991) |
|
Languages:
|
Thai, English (secondary language of the elite), ethnic and regional dialects |
|
Literacy:
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 96% male: 97.5% female: 94.6% (2003 est.) |
| Government | Thailand |
|
Country name:
|
conventional long form: Kingdom of Thailand
conventional short form: Thailand former: Siam |
|
Government type:
|
constitutional monarchy |
|
Capital:
|
Bangkok |
|
Administrative divisions:
|
76 provinces (changwat, singular and plural); Amnat Charoen, Ang Thong, Buriram, Chachoengsao, Chai Nat, Chaiyaphum, Chanthaburi, Chiang Mai, Chiang Rai, Chon Buri, Chumphon, Kalasin, Kamphaeng Phet, Kanchanaburi, Khon Kaen, Krabi, Krung Thep Mahanakhon (Bangkok), Lampang, Lamphun, Loei, Lop Buri, Mae Hong Son, Maha Sarakham, Mukdahan, Nakhon Nayok, Nakhon Pathom, Nakhon Phanom, Nakhon Ratchasima, Nakhon Sawan, Nakhon Si Thammarat, Nan, Narathiwat, Nong Bua Lamphu, Nong Khai, Nonthaburi, Pathum Thani, Pattani, Phangnga, Phatthalung, Phayao, Phetchabun, Phetchaburi, Phichit, Phitsanulok, Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya, Phrae, Phuket, Prachin Buri, Prachuap Khiri Khan, Ranong, Ratchaburi, Rayong, Roi Et, Sa Kaeo, Sakon Nakhon, Samut Prakan, Samut Sakhon, Samut Songkhram, Sara Buri, Satun, Sing Buri, Sisaket, Songkhla, Sukhothai, Suphan Buri, Surat Thani, Surin, Tak, Trang, Trat, Ubon Ratchathani, Udon Thani, Uthai Thani, Uttaradit, Yala, Yasothon |
|
Independence:
|
1238 (traditional founding date; never colonized) |
|
National holiday:
|
Birthday of King PHUMIPHON, 5 December (1927) |
|
Constitution:
|
new constitution signed by King PHUMIPHON on 11 October 1997 |
|
Legal system:
|
based on civil law system, with influences of common law; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction |
|
Suffrage:
|
18 years of age; universal and compulsory |
|
Executive branch:
|
chief of state: King PHUMIPHON Adunyadet (since 9 June 1946)
note: there is also a Privy Council head of government: Prime Minister THAKSIN Chinnawat (since 9 February 2001) and Deputy Prime Ministers Gen. (Ret.) CHAWALIT Yongchaiyut, KON Thappharansi, SUWIT Khunkitti, CHATURON Chaisaeng, VISHANU Krua-ngam, and PROMMIN Lertsuridej (since 18 February 2001) cabinet: Council of Ministers elections: none; the monarch is hereditary; prime minister is designated from among the members of the House of Representatives; following national elections for the House of Representatives, the leader of the party that can organize a majority coalition usually is appointed prime minister by the king |
|
Legislative branch:
|
bicameral National Assembly or Rathasapha consists of the Senate or Wuthisapha (200 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve four-year terms) and the House of Representatives or Sapha Phuthaen Ratsadon (500 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve four-year terms)
elections: Senate - last held 4 March, 29 April, 4 June, 9 July, and 22 July 2000 (next to be held NA March 2004); House of Representatives - last held 6 January 2001 (next to be held NA January 2005) election results: Senate - percent of vote by party - NA%; seats by party - NA; House of Representatives - percent of vote by party - NA%; seats by party - TRT 248, DP 128, TNP 41, NDP 29, other 54 |
|
Judicial branch:
|
Supreme Court or Sandika (judges appointed by the monarch) |
|
Political parties and leaders:
|
Democratic Party or DP (Prachathipat Party) [BANTADTAN Banyat]; National Development Party or NDP (Chat Phattana) [KORN Dabbaransi]; Thai Nation Party or TNP (Chat Thai Party) [BANHAN Sinlapa-acha]; Thai Rak Thai Party or TRT [THAKSIN Chinnawat] |
|
Political pressure groups and leaders:
|
NA |
|
International organization participation:
|
APEC, ARF, AsDB, ASEAN, BIS, CP, ESCAP, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICCt (signatory), ICFTU, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, ISO, ITU, NAM, OAS (observer), OIC (observer), OPCW, OSCE (partner), PCA, UN, UNAMSIL, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIKOM, UNMIBH, UNMISET, UNU, UPU, WCL, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WToO, WTrO |
|
Diplomatic representation in the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador SAKTHIP Krairiksh
consulate(s) general: Chicago, Los Angeles, and New York FAX: [1] (202) 944-3611 telephone: [1] (202) 944-3600 chancery: 1024 Wisconsin Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20007 |
|
Diplomatic representation from the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Darryl N. JOHNSON
embassy: 120/22 Wireless Road, Bangkok mailing address: APO AP 96546 telephone: [66] (2) 205-4000 FAX: [66] (2) 254-2990, 205-4131 consulate(s) general: Chiang Mai |
|
Flag description:
|
five horizontal bands of red (top), white, blue (double width), white, and red |
| Economy | Thailand |
|
Economy - overview:
|
Thailand has a free enterprise economy and welcomes foreign investment. Exports feature computers and electrical appliances. After enjoying the world's highest growth rate from 1985 to 1995 - averaging almost 9% annually - increased speculative pressure on Thailand's currency in 1997 led to a crisis that uncovered financial sector weaknesses and forced the government to float the baht. Long pegged at 25 to the dollar, the baht reached its lowest point of 56 to the dollar in January 1998, and the economy contracted by 10.2% that same year. Thailand then entered a recovery stage, expanding by 4.2% in 1999 and 4.4% in 2000, largely due to strong exports. An ailing financial sector and the slow pace of corporate debt restructuring, combined with a softening of global demand, slowed growth to 1.4% in 2001. Increased consumption and investment spending pushed GDP growth up to 5.2% in 2002 despite a sluggish global economy. |
|
GDP:
|
purchasing power parity - $445.8 billion (2002 est.) |
|
GDP - real growth rate:
|
5.3% (2002 est.) |
|
GDP - per capita:
|
purchasing power parity - $7,000 (2002 est.) |
|
GDP - composition by sector:
|
agriculture: 11%
industry: 40% services: 49% (2001) |
|
Population below poverty line:
|
12.5% (1998 est.) |
|
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
|
lowest 10%: 2.8%
highest 10%: 32.4% (1998) |
|
Distribution of family income - Gini index:
|
41.4 (1998) |
|
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
|
0.6% (2002 est.) |
|
Labor force:
|
33.4 million (2001 est.) |
|
Labor force - by occupation:
|
agriculture 54%, industry 15%, services 31% (1996 est.) |
|
Unemployment rate:
|
2.9% (2002 est.) |
|
Budget:
|
revenues: $19 billion
expenditures: $21 billion, including capital expenditures of $NA (2000 est.) |
|
Industries:
|
tourism; textiles and garments, agricultural processing, beverages, tobacco, cement, light manufacturing, such as jewelry; electric appliances and components, computers and parts, integrated circuits, furniture, plastics; world's second-largest tungsten producer and third-largest tin producer |
|
Industrial production growth rate:
|
3% (2000 est.) |
|
Electricity - production:
|
97.6 billion kWh (2001) |
|
Electricity - production by source:
|
fossil fuel: 91.3%
hydro: 6.4% other: 2.4% (2001) nuclear: 0% |
|
Electricity - consumption:
|
90.91 billion kWh (2001) |
|
Electricity - exports:
|
200 million kWh (2001) |
|
Electricity - imports:
|
350 million kWh (2001) |
|
Oil - production:
|
173,800 bbl/day (2001 est.) |
|
Oil - consumption:
|
785,000 bbl/day (2001 est.) |
|
Oil - exports:
|
NA (2001) |
|
Oil - imports:
|
NA (2001) |
|
Oil - proved reserves:
|
551.5 million bbl (37257) |
|
Natural gas - production:
|
18.73 billion cu m (2001 est.) |
|
Natural gas - consumption:
|
23.93 billion cu m (2001 est.) |
|
Natural gas - exports:
|
0 cu m (2001 est.) |
|
Natural gas - imports:
|
5.2 billion cu m (2001 est.) |
|
Natural gas - proved reserves:
|
368.2 billion cu m (37257) |
|
Agriculture - products:
|
rice, cassava (tapioca), rubber, corn, sugarcane, coconuts, soybeans |
|
Exports:
|
$67.7 billion f.o.b. (2002 est.) |
|
Exports - commodities:
|
computers, transistors, seafood, clothing, rice (2000) |
|
Exports - partners:
|
US 19.6%, Japan 14.5%, Singapore 8.1%, Hong Kong 5.4%, China 5.2%, Malaysia 4.1% (2002) |
|
Imports:
|
$58.1 billion f.o.b. (2002 est.) |
|
Imports - commodities:
|
capital goods, intermediate goods and raw materials, consumer goods, fuels (2000) |
|
Imports - partners:
|
Japan 23%, US 9.6%, China 7.6%, Malaysia 5.6%, Singapore 4.5%, Taiwan 4.4% (2002) |
|
Debt - external:
|
$62.5 billion (2002 est.) |
|
Economic aid - recipient:
|
$131.5 million (1998 est.) |
|
Currency:
|
baht (THB) |
|
Currency code:
|
THB |
|
Exchange rates:
|
baht per US dollar - 42.96 (2002), 44.43 (2001), 40.11 (2000), 37.81 (1999), 41.36 (1998) |
|
Fiscal year:
|
1 October - 30 September |
| Communications | Thailand |
|
Telephones - main lines in use:
|
5.6 million (2000) |
|
Telephones - mobile cellular:
|
3.1 million (2002) |
|
Telephone system:
|
general assessment: service to general public adequate, but investment in technological upgrades reduced by recession; bulk of service to government activities provided by multichannel cable and microwave radio relay network
domestic: microwave radio relay and multichannel cable; domestic satellite system being developed international: satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (1 Indian Ocean and 1 Pacific Ocean) |
|
Radio broadcast stations:
|
AM 204, FM 334, shortwave 6 (1999) |
|
Radios:
|
13.96 million (1997) |
|
Television broadcast stations:
|
5 (all in Bangkok; plus 131 repeaters) (1997) |
|
Televisions:
|
15.19 million (1997) |
|
Internet country code:
|
.th |
|
Internet Service Providers (ISPs):
|
15 (2000) |
|
Internet users:
|
1.2 million (2001) |
| Transportation | Thailand |
|
Railways:
|
total: 4,071 km
narrow gauge: 4,071 km 1.000-m gauge (2002) |
|
Highways:
|
total: 64,600 km
paved: 62,985 km unpaved: 1,615 km (1999 est.) |
|
Waterways:
|
4,000 km
note: 3,701 km are navigable throughout the year by boats with drafts up to 0.9 meters; numerous minor waterways serve shallow-draft native craft |
|
Pipelines:
|
gas 3,066 km; refined products 265 km (2003) |
|
Ports and harbors:
|
Bangkok, Laem Chabang, Pattani, Phuket, Sattahip, Si Racha, Songkhla |
|
Merchant marine:
|
total: 317 ships (1,000 GRT or over) 1,744,103 GRT/2,657,666 DWT
note: includes some foreign-owned ships registered here as a flag of convenience: Germany 1, Greece 1, Indonesia 1, Japan 1, Norway 24, Panama 1, Singapore 1 (2002 est.) ships by type: bulk 33, cargo 136, chemical tanker 5, combination bulk 1, combination ore/oil 1, container 17, liquefied gas 21, multi-functional large-load carrier 2, passenger 1, petroleum tanker 74, refrigerated cargo 17, roll on/roll off 2, short-sea passenger 2, specialized tanker 4, vehicle carrier 1 |
|
Airports:
|
111 (2002) |
|
Airports - with paved runways:
|
total: 62
over 3,047 m: 7 2,438 to 3,047 m: 10 914 to 1,523 m: 17 under 914 m: 5 (2002) 1,524 to 2,437 m: 23 |
|
Airports - with unpaved runways:
|
total: 49
1,524 to 2,437 m: 1 914 to 1,523 m: 17 under 914 m: 31 (2002) |
|
Heliports:
|
2 (2002) |
| Military | Thailand |
|
Military branches:
|
Royal Thai Army, Royal Thai Navy (includes Royal Thai Marine Corps), Royal Thai Air Force, paramilitary forces (includes the Border Patrol Police [including Police Aerial Reinforcement Unit], Thahan Phran, Special Action Forces, Police Aviation Division, Thai Marine Police, and the Volunteer Defense Corps) |
|
Military manpower - military age:
|
18 years of age (2003 est.) |
|
Military manpower - availability:
|
males age 15-49: 17,904,298 (2003 est.) |
|
Military manpower - fit for military service:
|
males age 15-49: 10,724,565 (2003 est.) |
|
Military manpower - reaching military age annually:
|
males: 520,472 (2003 est.) |
|
Military expenditures - dollar figure:
|
$1.775 billion (FY00) |
|
Military expenditures - percent of GDP:
|
1.4% (FY00) |
| Transnational Issues | Thailand |
|
Disputes - international:
|
completion of boundary demarcation with Cambodia hampered by accusations of moving and destroying boundary markers, encroachments, initiating border incidents, and sealing off Preah Vihear temple ruins, awarded to Cambodia by ICJ decision in 1962; demarcation complete except for a 1 kilometer segment at the mouth of the Kolok River in dispute with Malaysia; demarcation with Laos complete except for certain Mekong River islets and complaints of Thai squatters; despite continuing border committee talks, significant differences remain with Burma over boundary alignment and the handling of ethnic rebels, refugees, and illegal cross-border activities |
|
Illicit drugs:
|
a minor producer of opium, heroin, and marijuana; illicit transit point for heroin en route to the international drug market from Burma and Laos; eradication efforts have reduced the area of cannabis cultivation and shifted some production to neighboring countries; opium poppy cultivation has been reduced by eradication efforts; also a drug money-laundering center; minor role in amphetamine production for regional consumption; increasing indigenous abuse of methamphetamine |
|
This page was last updated on 18 December, 2003 |