

| The World Factbook | ||


|
Johnston Atoll |

|
|
| Introduction | Johnston Atoll |
|
Background:
|
Both the US and the Kingdom of Hawaii annexed Johnston Atoll in 1858, but it was the US that mined the guano deposits until the late 1880s. The US Navy took over the atoll in 1934, and subsequently the US Air Force assumed control in 1948. The site was used for high-altitude nuclear tests in the 1950s and 1960s, and until late in 2000 the atoll was maintained as a storage and disposal site for chemical weapons. Munitions destruction is now complete. Cleanup and closure of the facility is progressing, with completion anticipated in 2004. |
| Geography | Johnston Atoll |
|
Location:
|
Oceania, atoll in the North Pacific Ocean 717 NM (1328 km) southwest of Honolulu, Hawaii, about one-third of the way from Hawaii to the Marshall Islands |
|
Geographic coordinates:
|
16 45 N, 169 31 W |
|
Map references:
|
Oceania |
|
Area:
|
total: 2.8 sq km
water: 0 sq km land: 2.8 sq km |
|
Area - comparative:
|
about 4.7 times the size of The Mall in Washington, DC |
|
Land boundaries:
|
0 km |
|
Coastline:
|
34 km |
|
Maritime claims:
|
exclusive economic zone: 200 NM
territorial sea: 12 NM |
|
Climate:
|
tropical, but generally dry; consistent northeast trade winds with little seasonal temperature variation |
|
Terrain:
|
mostly flat |
|
Elevation extremes:
|
lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m
highest point: Summit Peak 5 m |
|
Natural resources:
|
guano deposits worked until depletion about 1890, terrestrial and aquatic wildlife |
|
Land use:
|
arable land: 0%
permanent crops: 0% other: 100% (1998 est.) |
|
Irrigated land:
|
0 sq km (1998 est.) |
|
Natural hazards:
|
NA |
|
Environment - current issues:
|
no natural fresh water resources |
|
Geography - note:
|
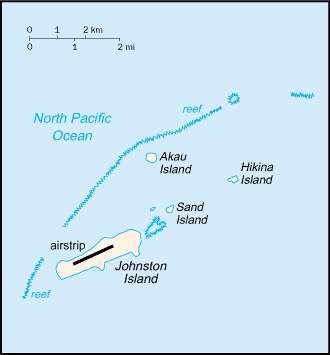
strategic location in the North Pacific Ocean; Johnston Island and Sand Island are natural islands, which have been expanded by coral dredging; North Island (Akau) and East Island (Hikina) are manmade islands formed from coral dredging; the egg-shaped reef is 34 km in circumference; closed to the public; a former US nuclear weapons test site; site of Johnston Atoll Chemical Agent Disposal System (JACADS); some low-growing vegetation |
| People | Johnston Atoll |
|
Population:
|
no indigenous inhabitants
note: in previous years, there was an average of 1,100 US military and civilian contractor personnel present; as of September 2001, population had decreased significantly when US Army Chemical Activity Pacific (USACAP) departed; as of January 2003 the island population was just above 800 personnel, including US Air Force, US Department of Defense civilian, and civilian contractor personnel (January 2003 est.) (July 2003 est.) |
| Government | Johnston Atoll |
|
Country name:
|
conventional long form: none
conventional short form: Johnston Atoll |
|
Dependency status:
|
unincorporated territory of the US; administered from Honolulu, HI, by Pacific Air Forces, Hickam Air Force Base, and the Fish and Wildlife Service of the US Department of the Interior as part of the National Wildlife Refuge system |
|
Legal system:
|
the laws of the US, where applicable, apply |
|
Flag description:
|
the flag of the US is used |
| Economy | Johnston Atoll |
|
Economy - overview:
|
Economic activity is limited to providing services to US military personnel and contractors located on the island. All food and manufactured goods must be imported. |
|
Electricity - production:
|
44.2 million kWh; note - approximate annual production; there are six 25,000 kWh generators operated by the base operating support contractor (1999) |
|
Electricity - consumption:
|
2.002 million kWh; note - approximate annual consumption |
| Communications | Johnston Atoll |
|
Telephone system:
|
general assessment: 33 commercial lines, 15 incoming and 18 outgoing; adequate telecommunications
domestic: 60-channel submarine cable (broken in January 2002), 24 DSN circuits by satellite, Automated Digital Network (AUTODIN) with standard remote terminal, digital telephone switch, Military Affiliated Radio System (MARS) station (scheduled for decommissioning March 2003), UHF/VHF air-ground radio, a link to the Pacific Consolidated Telecommunications Network (PCTN) satellite international: NA (2002) |
|
Radio broadcast stations:
|
AM NA, FM 7 (1 island-run morale, welfare, and recreation station and 6 all-music digital radio stations broadcast over FM band), shortwave NA (2002) |
|
Television broadcast stations:
|
commercial satellite television system, with 30 channels (2002) |
|
Internet Service Providers (ISPs):
|
1 256 KB circuit to US Department of Defense-run Nonsecure Internet Protocol Router Network (NIPRNET) (2002) |
| Transportation | Johnston Atoll |
|
Waterways:
|
none |
|
Ports and harbors:
|
Johnston Island |
|
Airports:
|
1 (2002) |
|
Airports - with paved runways:
|
total: 1
2,438 to 3,047 m: 1 (2002) |
| Military | Johnston Atoll |
|
Military - note:
|
defense is the responsibility of the US |
| Transnational Issues | Johnston Atoll |
|
Disputes - international:
|
none |
|
This page was last updated on 18 December, 2003 |