

| The World Factbook 2002 | ||


|
New Zealand |

|
|
| Introduction | New Zealand |
|
Background:
|
The British colony of New Zealand became an independent dominion in 1907 and supported the UK militarily in both World Wars. New Zealand's full participation in number of defense alliances lapsed by the 1980s. In recent years the government has sought to address longstanding native Maori grievances. |
| Geography | New Zealand |
|
Location:
|
Oceania, islands in the South Pacific Ocean, southeast of Australia |
|
Geographic coordinates:
|
41 00 S, 174 00 E |
|
Map references:
|
Oceania |
|
Area:
|
total: 268,680 sq km
note: includes Antipodes Islands, Auckland Islands, Bounty Islands, Campbell Island, Chatham Islands, and Kermadec Islands water: NA sq km land: NA sq km |
|
Area - comparative:
|
about the size of Colorado |
|
Land boundaries:
|
0 km |
|
Coastline:
|
15,134 km |
|
Maritime claims:
|
continental shelf: 200 NM or to the edge of the continental margin
territorial sea: 12 NM exclusive economic zone: 200 NM |
|
Climate:
|
temperate with sharp regional contrasts |
|
Terrain:
|
predominately mountainous with some large coastal plains |
|
Elevation extremes:
|
lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m
highest point: Mount Cook 3,764 m |
|
Natural resources:
|
natural gas, iron ore, sand, coal, timber, hydropower, gold, limestone |
|
Land use:
|
arable land: 6%
permanent crops: 6% other: 88% (1998 est.) |
|
Irrigated land:
|
2,850 sq km (1998 est.) |
|
Natural hazards:
|
earthquakes are common, though usually not severe; volcanic activity |
|
Environment - current issues:
|
deforestation; soil erosion; native flora and fauna hard-hit by species introduced from outside |
|
Environment - international agreements:
|
party to: Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: Antarctic Seals, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Marine Life Conservation |
|
Geography - note:
|
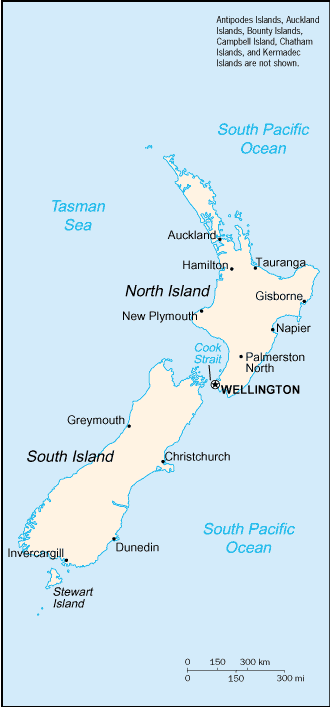
about 80% of the population lives in cities; Wellington is the southernmost national capital in the world |
| People | New Zealand |
|
Population:
|
3,908,037 (July 2002 est.) |
|
Age structure:
|
0-14 years: 22.2% (male 443,921; female 422,804)
15-64 years: 66.3% (male 1,299,973; female 1,290,097) 65 years and over: 11.5% (male 196,640; female 254,602) (2002 est.) |
|
Population growth rate:
|
1.12% (2002 est.) |
|
Birth rate:
|
14.23 births/1,000 population (2002 est.) |
|
Death rate:
|
7.55 deaths/1,000 population (2002 est.) |
|
Net migration rate:
|
4.48 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2002 est.) |
|
Sex ratio:
|
at birth: 1.04 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.05 male(s)/female 15-64 years: 1.01 male(s)/female 65 years and over: 0.77 male(s)/female total population: 0.99 male(s)/female (2002 est.) |
|
Infant mortality rate:
|
6.18 deaths/1,000 live births (2002 est.) |
|
Life expectancy at birth:
|
total population: 78.15 years
female: 81.27 years (2002 est.) male: 75.17 years |
|
Total fertility rate:
|
1.8 children born/woman (2002 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:
|
0.06% (1999 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:
|
1,200 (1999 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - deaths:
|
less than 100 (1999 est.) |
|
Nationality:
|
noun: New Zealander(s)
adjective: New Zealand |
|
Ethnic groups:
|
New Zealand European 74.5%, Maori 9.7%, other European 4.6%, Pacific Islander 3.8%, Asian and others 7.4% |
|
Religions:
|
Anglican 24%, Presbyterian 18%, Roman Catholic 15%, Methodist 5%, Baptist 2%, other Protestant 3%, unspecified or none 33% (1986) |
|
Languages:
|
English (official), Maori (official) |
|
Literacy:
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 99% (1980 est.) male: NA% female: NA% |
| Government | New Zealand |
|
Country name:
|
conventional long form: none
conventional short form: New Zealand abbreviation: NZ |
|
Government type:
|
parliamentary democracy |
|
Capital:
|
Wellington |
|
Administrative divisions:
|
93 counties, 9 districts*, and 3 town districts**; Akaroa, Amuri, Ashburton, Bay of Islands, Bruce, Buller, Chatham Islands, Cheviot, Clifton, Clutha, Cook, Dannevirke, Egmont, Eketahuna, Ellesmere, Eltham, Eyre, Featherston, Franklin, Golden Bay, Great Barrier Island, Grey, Hauraki Plains, Hawera*, Hawke's Bay, Heathcote, Hikurangi**, Hobson, Hokianga, Horowhenua, Hurunui, Hutt, Inangahua, Inglewood, Kaikoura, Kairanga, Kiwitea, Lake, Mackenzie, Malvern, Manaia**, Manawatu, Mangonui, Maniototo, Marlborough, Masterton, Matamata, Mount Herbert, Ohinemuri, Opotiki, Oroua, Otamatea, Otorohanga*, Oxford, Pahiatua, Paparua, Patea, Piako, Pohangina, Raglan, Rangiora*, Rangitikei, Rodney, Rotorua*, Runanga, Saint Kilda, Silverpeaks, Southland, Stewart Island, Stratford, Strathallan, Taranaki, Taumarunui, Taupo, Tauranga, Thames-Coromandel*, Tuapeka, Vincent, Waiapu, Waiheke, Waihemo, Waikato, Waikohu, Waimairi, Waimarino, Waimate, Waimate West, Waimea, Waipa, Waipawa*, Waipukurau*, Wairarapa South, Wairewa, Wairoa, Waitaki, Waitomo*, Waitotara, Wallace, Wanganui, Waverley**, Westland, Whakatane*, Whangarei, Whangaroa, Woodville
note: there may be a new administrative structure of 16 regions (Auckland, Bay of Plenty, Canterbury, Gisborne, Hawke's Bay, Marlborough, Nelson, Northland, Otago, Southland, Taranaki, Tasman, Waikato, Wanganui-Manawatu, Wellington, West Coast) that are subdivided into 57 districts and 16 cities* (Ashburton, Auckland*, Banks Peninsula, Buller, Carterton, Central Hawke's Bay, Central Otago, Christchurch*, Clutha, Dunedin*, Far North, Franklin, Gisborne, Gore, Grey, Hamilton*, Hastings, Hauraki, Horowhenua, Hurunui, Hutt*, Invercargill*, Kaikoura, Kaipara, Kapiti Coast, Kawerau, Mackenzie, Manawatu, Manukau*, Marlborough, Masterton, Matamata Piako, Napier*, Nelson*, New Plymouth, North Shore*, Opotiki, Otorohanga, Palmerston North*, Papakura*, Porirua*, Queenstown Lakes, Rangitikei, Rodney, Rotorua, Ruapehu, Selwyn, Southland, South Taranaki, South Waikato, South Wairarapa, Stratford, Tararua, Tasman, Taupo, Tauranga, Thames Coromandel, Timaru, Upper Hutt*, Waikato, Waimakariri, Waimate, Waipa, Wairoa, Waitakere*, Waitaki, Waitomo, Wanganui, Wellington*, Western Bay of Plenty, Westland, Whakatane, Whangarei) |
|
Dependent areas:
|
Cook Islands, Niue, Tokelau |
|
Independence:
|
26 September 1907 (from UK) |
|
National holiday:
|
Waitangi Day (Treaty of Waitangi established British sovereignty over New Zealand), 6 February (1840) |
|
Constitution:
|
consists of a series of legal documents, including certain acts of the UK and New Zealand Parliaments and The Constitution Act 1986 which is the principal formal charter |
|
Legal system:
|
based on English law, with special land legislation and land courts for Maoris; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction, with reservations |
|
Suffrage:
|
18 years of age; universal |
|
Executive branch:
|
chief of state: Queen ELIZABETH II (since 6 February 1952), represented by Governor General Dame Silvia CARTWRIGHT (since 4 April 2001)
head of government: Prime Minister Helen CLARK (since 10 December 1999) and Deputy Prime Minister James (Jim) ANDERTON (since 10 December 1999) cabinet: Executive Council appointed by the governor general on the recommendation of the prime minister elections: none; the monarch is hereditary; governor general appointed by the monarch; following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or the leader of a majority coalition is usually appointed prime minister by the governor general for a three-year term; deputy prime minister appointed by the governor general |
|
Legislative branch:
|
unicameral House of Representatives - commonly called Parliament (120 seats; members elected by popular vote in single-member constituencies to serve three-year terms)
elections: last held 27 November 1999 (next must be called by November 2002) election results: percent of vote by party - NA%; seats by party - NZLP 49, NP 39, Alliance 10, ACT New Zealand 9, Green Party 7, NZFP 5, UNZ 1 note: NZLP and Alliance formed the government coalition; the National Party is the opposition party |
|
Judicial branch:
|
High Court; Court of Appeal |
|
Political parties and leaders:
|
ACT, New Zealand [Richard PREBBLE]; Alliance (a coalition of the New Labor Party, Democratic Party, New Zealand Liberal Party, and Mana Motuhake) [James (Jim) ANDERTON]; Green Party [Jeanette FITZSIMONS and Rod DONALD]; National Party or NP [William (Bill) English]; New Zealand First Party or NZFP [Winston PETERS]; New Zealand Labor Party or NZLP [Helen CLARK]; United New Zealand or UNZ [Peter DUNNE] |
|
Political pressure groups and leaders:
|
NA |
|
International organization participation:
|
ABEDA, ANZUS (US suspended security obligations to NZ on 11 August 1986), APEC, ARF (dialogue partner), AsDB, ASEAN (dialogue partner), Australia Group, C, CCC, CP, EBRD, ESCAP, FAO, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICFTU, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM (observer), ISO, ITU, NAM (guest), NSG, OECD, OPCW, PCA, Sparteca, SPC, SPF, UN, UNAMSIL, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNMOP, UNTAET, UNTSO, UPU, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTrO |
|
Diplomatic representation in the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador L. John WOOD
chancery: 37 Observatory Circle NW, Washington, DC 20008 FAX: [1] (202) 667-5227 consulate(s) general: Los Angeles, New York telephone: [1] (202) 328-4800 |
|
Diplomatic representation from the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Charles J. SWINDELLS
embassy: 29 Fitzherbert Terrace, Thorndon, Wellington mailing address: P. O. Box 1190, Wellington; PSC 467, Box 1, FPO AP 96531-1001 telephone: [64] (4) 462-6000 FAX: [64] (4) 478-1701 consulate(s) general: Auckland |
|
Flag description:
|
blue with the flag of the UK in the upper hoist-side quadrant with four red five-pointed stars edged in white centered in the outer half of the flag; the stars represent the Southern Cross constellation |
| Economy | New Zealand |
|
Economy - overview:
|
Since 1984 the government has accomplished major economic restructuring, transforming New Zealand from an agrarian economy dependent on concessionary British market access to a more industrialized, free market economy that can compete globally. This dynamic growth has boosted real incomes (but left behind many at the bottom of the ladder), broadened and deepened the technological capabilities of the industrial sector, and contained inflationary pressures. While per capita incomes have been rising, however, they remain below the level of the four largest EU economies, and there is some government concern that New Zealand is not closing the gap. New Zealand is heavily dependent on trade - particularly in agricultural products - to drive growth, and it has been affected by the global economic slowdown and the slump in commodity prices. Thus far the New Zealand economy has been relatively resilient, achieving about 3% growth in 2001, but the New Zealand business cycle tends to lag the US cycle by about six months, so the worst of the downturn may not hit until mid-2002. |
|
GDP:
|
purchasing power parity - $75.4 billion (2001 est.) |
|
GDP - real growth rate:
|
3.1% (2001 est.) |
|
GDP - per capita:
|
purchasing power parity - $19,500 (2001 est.) |
|
GDP - composition by sector:
|
agriculture: 8%
industry: 23% services: 69% (1999) |
|
Population below poverty line:
|
NA% |
|
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
|
lowest 10%: 0.3%
highest 10%: 29.8% (1991 est.) |
|
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
|
2.6% (2001 est.) |
|
Labor force:
|
1.92 million (2001 est.) |
|
Labor force - by occupation:
|
services 65%, industry 25%, agriculture 10% (1995) |
|
Unemployment rate:
|
5.5% (2001 est.) |
|
Budget:
|
revenues: $16.7 billion
expenditures: $16.6 billion, including capital expenditures of $NA (FY00/01) |
|
Industries:
|
food processing, wood and paper products, textiles, machinery, transportation equipment, banking and insurance, tourism, mining |
|
Industrial production growth rate:
|
3% (2001 est.) |
|
Electricity - production:
|
35.823 billion kWh (2000) |
|
Electricity - production by source:
|
fossil fuel: 26.55%
hydro: 66.45% other: 7% (2000) nuclear: 0% |
|
Electricity - consumption:
|
33.315 billion kWh (2000) |
|
Electricity - exports:
|
0 kWh (2000) |
|
Electricity - imports:
|
0 kWh (2000) |
|
Agriculture - products:
|
wheat, barley, potatoes, pulses, fruits, vegetables; wool, beef, dairy products; fish |
|
Exports:
|
$14.2 billion (2001 est.) |
|
Exports - commodities:
|
dairy products, meat, wood and wood products, fish, machinery |
|
Exports - partners:
|
Australia 20.4%, US 14.5%, Japan 13.5%, UK 5.4%, South Korea, China (2000) |
|
Imports:
|
$12.5 billion (2001 est.) |
|
Imports - commodities:
|
machinery and equipment, vehicles and aircraft, petroleum, electronics, textiles, plastics |
|
Imports - partners:
|
Australia 22.5%, US 17.5%, Japan 11%, UK 4%, China, Germany (2000) |
|
Debt - external:
|
$31.1 billion (2001 est.) |
|
Economic aid - donor:
|
ODA, $99.7 million (FY00/01) |
|
Currency:
|
New Zealand dollar (NZD) |
|
Currency code:
|
NZD |
|
Exchange rates:
|
New Zealand dollars per US dollar - 2.3535 (January 2002), 2.3776 (2001), 2.1863 (2000), 1.8886 (1999), 1.8632 (1998), 1.5083 (1997) |
|
Fiscal year:
|
1 July - 30 June |
| Communications | New Zealand |
|
Telephones - main lines in use:
|
1.92 million (2000) |
|
Telephones - mobile cellular:
|
2.2 million (2000) |
|
Telephone system:
|
general assessment: excellent domestic and international systems
domestic: NA international: submarine cables to Australia and Fiji; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (Pacific Ocean) |
|
Radio broadcast stations:
|
AM 124, FM 290, shortwave 4 (1998) |
|
Radios:
|
3.75 million (1997) |
|
Television broadcast stations:
|
41 (plus 52 medium-power repeaters and over 650 low-power repeaters) (1997) |
|
Televisions:
|
1.926 million (1997) |
|
Internet country code:
|
.nz |
|
Internet Service Providers (ISPs):
|
36 (2000) |
|
Internet users:
|
1.78 million (2001) |
| Transportation | New Zealand |
|
Railways:
|
total: 3,908 km
narrow gauge: 3,908 km 1.067-m gauge (506 km electrified) (2001) |
|
Highways:
|
total: 92,200 km
paved: 53,568 km (including at least 144 km of expressways) unpaved: 38,632 km (1996) |
|
Waterways:
|
1,609 km
note: of little importance in satisfying total transportation requirements |
|
Pipelines:
|
petroleum products 160 km; natural gas 1,000 km; liquefied petroleum gas or LPG 150 km |
|
Ports and harbors:
|
Auckland, Christchurch, Dunedin, Tauranga, Wellington |
|
Merchant marine:
|
total: 8 ships (1,000 GRT or over) totaling 68,427 GRT/106,627 DWT
note: includes a foreign-owned ship registered here as a flag of convenience: Australia 1 (2002 est.) ships by type: bulk 3, cargo 1, container 1, petroleum tanker 2, roll on/roll off 1 |
|
Airports:
|
106 (2001) |
|
Airports - with paved runways:
|
total: 44
over 3,047 m: 2 2,438 to 3,047 m: 1 914 to 1,523 m: 28 under 914 m: 3 (2001) 1,524 to 2,437 m: 10 |
|
Airports - with unpaved runways:
|
total: 62
1,524 to 2,437 m: 1 914 to 1,523 m: 24 under 914 m: 37 (2001) |
|
Heliports:
|
1 (2001) |
| Military | New Zealand |
|
Military branches:
|
New Zealand Army, Royal New Zealand Navy, Royal New Zealand Air Force |
|
Military manpower - military age:
|
20 years of age (2002 est.) |
|
Military manpower - availability:
|
males age 15-49: 1,010,316 (2002 est.) |
|
Military manpower - fit for military service:
|
males age 15-49: 850,185 (2002 est.) |
|
Military manpower - reaching military age annually:
|
males: 26,480 (2002 est.) |
|
Military expenditures - dollar figure:
|
$515.6 million (2002 est.) |
|
Military expenditures - percent of GDP:
|
1.2% (FY2001/02) |
| Transnational Issues | New Zealand |
|
Disputes - international:
|
territorial claim in Antarctica (Ross Dependency) |
|
This page was last updated on 1 January 2002 |